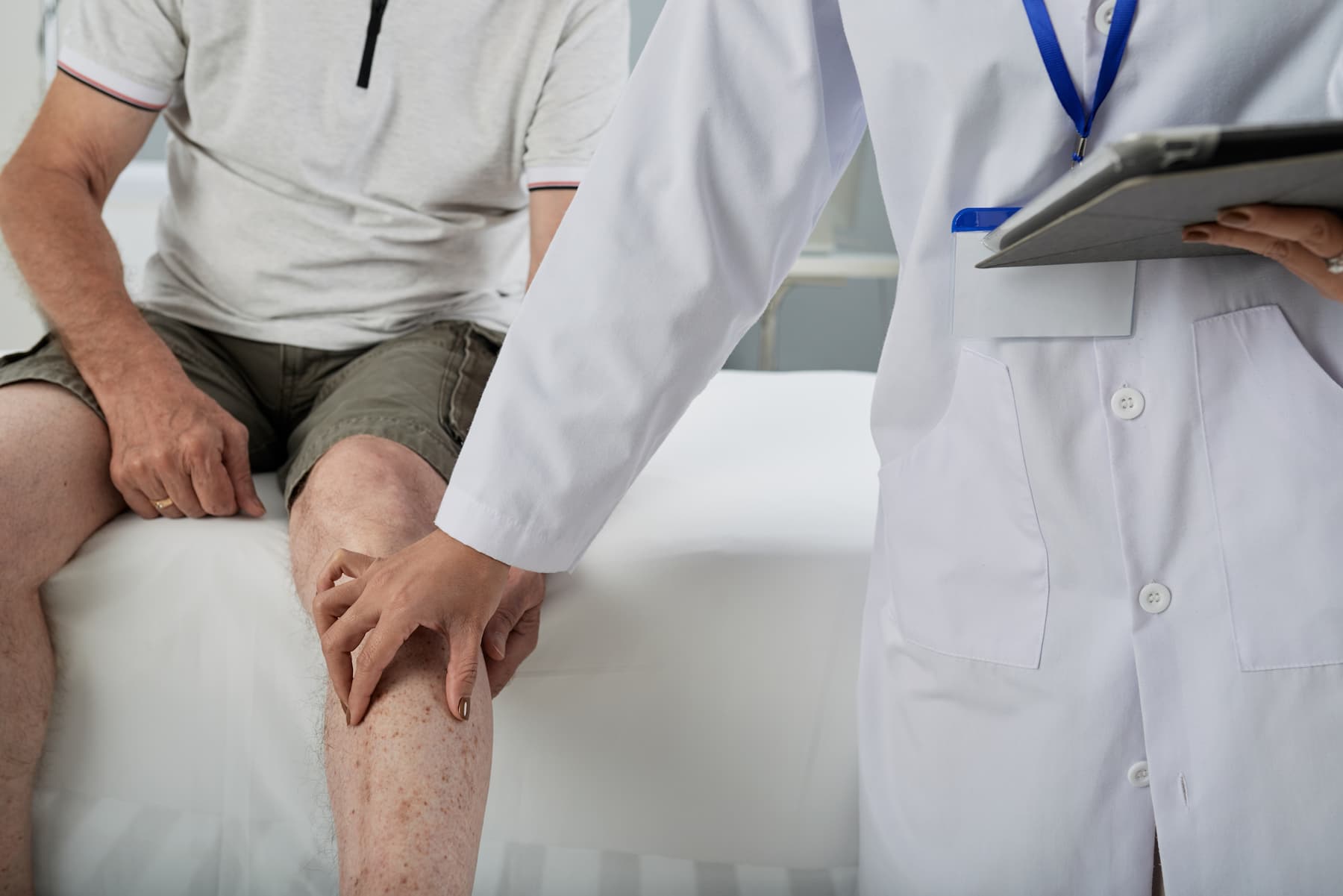
Gonarthrosis: what it is, treatment, surgery, exercise, diet
When articular cartilage deteriorates, gonarthrosis sets in. Find out how to help yourself.


Learn more about our editorial process
.

Learn more about our editorial process
.

Learn more about our editorial process
.

Learn more about our editorial process
.
Why you can trust us
Articles on Natu.Care are written based on scientific research, data from government websites and other reliable sources. The texts are written in cooperation with doctors, nutritionists and other health and beauty experts. Articles are reviewed before publication and during significant updates.
.Learn more about our editorial process
.Information about advertisements
Content on Natu.Care may contain links to products from the sale of which we may receive a commission. When creating content, we adhere to high editorial standards and take care to be objective about the products discussed. The presence of affiliate links is not dictated by our partners, and we select the products we review ourselves completely independently.
.Learn more about our terms and Conditions
.Good as it was. And now it is what it is -an orthopaedic surgeon I know used to say, looking at X-rays of knees affected by severe degenerative changes. And unfortunately he was quite right, because gonarthrosis is an irreversible, progressive disease.
.
But this does not at all mean that one should wring one's hands and wait for loss of function. On the contrary, orthopaedics has a number of methods that improve the quality of life of patients, reduce pain and restore fitness to those affected. After all, the aforementioned doctor, after this not very optimistic start, always added: But don't worry, we will do what we can to make it better.
.
From this article you will learn:
.- What gonarthrosis is and how its progression is assessed. .
- How the condition manifests itself. .
- What treatment methods are effective and most commonly used.
- What is the most common.
- Does diet have anything to do with gonarthrosis. .
- What, apart from medication and treatments, can help you. .

Sprawdź, jak może on zadbać o zdrowie Twoich stawów i urodę! Kolagen Premium (10 000 mg) wiśnia
Natu.Care Kolagen Premium Sport 10000 mg, wiśnia
Natu.Care Kolagen Premium dla zdrowia stawów, skóry, paznokci i włosów. Wołowy kolagen w optymalnej dawce 10 000 mg. Przebadany przez niezależne laboratorium.
Sprawdź cenę
Ten kolagen dobrze się rozpuszcza, super smakuje – jak taki soczek wiśniowy. Moje włosy przestały wypadać, są gęstsze i zdrowsze a cera promienna.@Dominika P.
See also:
.
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) .
- Knee pain - causes and treatment .
- Home remedies for knee pain
- Knees crunching and popping
- Baby ways for joints
- Tennis elbow
- Golfer's elbow
What is gonarthrosis?
.
Gonarthrosis is otherwise known as osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease of the knee. The condition involves the degradation of the articular cartilage that encases the bones that come into contact with each other.
Gonarthrosis is a condition in which the articular cartilage that encases the bones in contact with each other degrades.
When two surfaces come together and on top of that move - friction is created, which leads to damage (their surface will wear down). It would be exactly the same with bones if it were not for cartilage and joint fluid. These structures provide adequate glide and reduce friction.
There is a constant exchange of cells in your body - skin cells, for example, die (that's why we give ourselves a scrub - to get rid of used epidermis faster) and new cells form in their place. The cells of the cartilage tissues are also subject to this replacement process. Gonarthrosis begins when this mechanism is disrupted and cartilage cells die in greater numbers than they are formedand.
Simply put: cartilage destruction begins at the cellular level. However, once cartilage tissue is damaged, the body is unable to rebuild it at a fast enough rate.
When the surface of the cartilage is damaged, the bones begin to rub against each other.
During the dying/process of cartilage tissue destruction, the bones experience increasing loads during movement. This has several consequences: the subchondral bone undergoes neovascularisation (formation of new blood vessels) and increased cellularity. This causes the bone in this area to thicken and become more dense. This gives osteophytes the opportunity to grow..
 .
.
Kacper Nihalani doctor
.
As a result, so-called bone beaks, or osteophytes, begin to appear at the junction of the bones. These are lumps, growths and thickenings on the surface of the joint that grow larger and larger over the course of the disease and can lead to narrowing or complete disappearance of the space between the two bones that make up the joint (this space is called the joint space)and.
Osteophytes can also break off in this space and are then called 'joint mice'..

Kacper Nihalani doctor
.
Assessment of the condition of articular cartilage
.
Gonarthrosis is diagnosed on the basis of a patient interview, manual examination of the knee and imaging studies. The latter are necessary to determine how much damage is present in the joint. The Outerbridge and Kellgren-Lawrence scalesand.
are used to assess the severity of degenerative changes.
The former determines the degree of chondromalacia, or cartilage softening. Stages of the Outerbridge scale :
- 0 - no visible changes (normal cartilage), .
- I grade - softening of the surface, .
- II grade - cracks and fissures less than 1.25 mm, .
- III degree - full thickness cracks and fissures (greater than 1.25 mm) extending to the bone, .
- IV grade - defects in cartilage exposing bone, .
Chondromalacia of the cartilage is an ailment, occurring before and actually leading to gonarthrosis. Only its stage IV, which is loss of cartilage tissue exposing bone, is considered a degenerative change.
The second scale - Kellgren-Lawrence - is used to assess the severity of degenerative changes visible on radiographic examination (on rentgen). It already takes into account the changes in bone structure (osteophytes) that are characteristic of osteoarthritisand.
Stages of the Kellgren-Lawrence scale:
.
- 0 - joint with no visible changes, .
- 1 - minor osteophytes can be observed, .
- 2 - moderate osteophytes, .
- 3 - large osteophytic changes and narrowing of the articular crevices, .
- 4 - very large osteophytes and significant joint stomata narrowing or atrophy, .
Gonarthrosis - symptoms
.
Symptoms of knee osteoarthrosis include pain (affecting about 15% of people) when moving and putting pressure on the joint, and in advanced stages of the disease also at rest. In addition, stiffness of the joint, widening of its outline, change in the limb's axis and restriction of mobility, which leads to problems with walking.
Contrary to appearances, knee pain is not at all the most common symptom associated with gonarthrosis. According to a 2000 research paper published in The Journal of Rheumatology, only 15 per cent of patients who were found to have degenerative changes in the joint on imaging complained of associated painand.
.
The study cited in the article is cross-sectional, so in my opinion it is not strong scientific evidence. On top of that, in the 2014 article (a Vietnamese study), more than 30% of patients with knee pain had gonarthrosis. It is safer to say that the absence of pain does not mean there is no gonarthrosis. On the other hand, if pain is present, gonarthrosis is much more likely..
 .
.
Kacper Nihalani doctor
.
In addition to chronic knee pain, osteoarthritis in this joint can also manifest as stiffness and reduced mobility. If osteophytic changes on the bone surface are advanced, you may also notice irregularities on the knee surface during flexionand.
Gonarthrosis may also be accompanied by the presence of inflammation in the knee and the swelling caused by it .
.
Gonarthrosis - treatment
.
Treatment of gonarthrosis depends on the severity of the condition. Painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, physiotherapy, orthoses and stabilisers are available. In the most severe cases of knee osteoarthrosis, surgery may also be performed. Unfortunately, the condition is irreversible and treatment consists of symptom reliefand.
.
Today's knee replacement is the end treatment. Other forms of therapy are an effective method to protect the knee from so-called "replacement" for as long as possible..
 .
.
Kacper Nihalani doctor
.
Gonarthrosis versus surgery
.
In osteoarthritis of the knee, there are three types of surgery:
- artroscopy, .
- corrective osteotomy, .
- endoprosthesis, .
Arthroscopy in gonarthrosis
.
Theoretically, arthroscopy in gonarthrosis can be performed to mechanically clean the joint surfaces of osteophytes and flush the joint with saline. However, in a 2002 study involving 180 patients with gonarthrosis, this method was found to have no long-term healing effectand.
Patients were divided into three groups: the first was performed to cleanse the knee joint using arthroscopy, the second a lavage using the same method and the third was a placebo control group. Twenty-four months after the procedures, it was found that the rates of pain and joint mobility were similar in all three groupsand.
Currently, it is thought that arthroscopic procedures may do more harm than good in people with gonarthrosis. Adhesions are left behind after surgery, and arthroscopic procedures cannot address the cause of this conditionand.
Osteotomy for gonarthrosis
.
Corrective osteotomy involves correcting the axis of the limb. In gonarthrosis of the knee, it is carried out very rarely - mainly when the affected limb has an abnormal axis as a result of a fracture or a postural defect (knee scoliosis or valgus). The uneven alignment of the bones can cause excessive pressure and promote the development of degenerative changesand.
.
The disadvantage of this method is the need to immobilise the limb in a plaster cast for a long period of time.
.
Knee joint endoprosthesis
.
Gonarthrosis is one of the main indications for the implantation of a partial or total knee replacement (endoprosthesis). This procedure is performed at a very advanced stage of knee osteoarthrosis when other treatments are not satisfactoryand.
A total endoprosthesis is, as the name suggests, the replacement of a certain area (usually the medial) of the knee joint with an artificial equivalent. A total endoprosthesis involves the replacement of the entire jointand.
Knee replacement aims to restore the patient's function, i.e. the ability to use the joint normally. Although implanting an endoprosthesis sounds very serious, after surgery the patient is uprighted under the guidance of a physiotherapist and begins walking from day one - at first with the help of crutches .
.
People after surgery are supported by crutches for a few weeks or so, but it is common for younger patients to wean themselves off them sooner. Knee replacement is a procedure with a relatively low risk of complications, with the most common being pain at the front of the kneeand.
The patient should be walking independently after about 6 weeks. The sooner, the better, because then the risk of complications is reduced..

Kacper Nihalani doctor
Important
The knee replacement is inserted so that you can function normally. Once the periarticular structures have healed and you are off crutches, you can walk or cycle normally. Only sports that are extremely risky for the knees, i.e. extreme sports and, for example, skiing or snowboarding, are not recommended.
One of the most important factors in achieving the intended effect of an endoprosthesis is rehabilitation. The earlier you start it, the better. The right set of exercises and treatments complements the surgery. If you undergo it with commitment, you greatly increase your chances of returning to full fitness.
Physiotherapy in gonarthrosis
.
As we are already talking about physiotherapy, it is worth looking at it not only in terms of post-operative rehabilitation. Indeed, physiotherapy is a very important part of the treatment of knee osteoarthritis.
Correctly selected treatments and exercises can help you to reduce pain, improve joint mobility and slow the progression of the diseaseand.
.
Physiotherapy for gonarthrosis may includeand:
.
- ultrasound, .
- electrotherapy, .
- muscle stimulation, .
- cryotherapy, .
- special massage techniques, .
- dry needling, .
- stretching and strengthening exercises for the adductor muscles,
- special massage techniques.
- traction of joint surfaces, .
Medications for gonarthrosis
.
Among the pharmaceuticals used to treat gonarthrosis areand:
- analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), .
- glucocorticoids, .
- opioids, .
- low-acting drugs for osteoarthritis, .
The most commonly used drugs are painkillers and anti-inflammatory agents, or the popular NLPs. In the treatment of chronic ailments, the second-generation ones - which are less burdensome on the stomach - are used. However, even these are not inert to the body, so it is worth using other treatments to reduce the need to take them.
When treated with NSAIDs, you can also take omeprazole, for example, which has a protective effect on the gastric mucosa. But it is better not to take it on its own, as such drugs also have their side effects, such as hyponatraemia, i.e. low levels of sodium in the body..
 .
.
Kacper Nihalani doctor
.
Steroid injections on the other hand, are a much-loved option for patients, providing quick pain relief. Unfortunately, it is not recommended for long term use as steroids damage the surface of the joint and, looking at the long term, can do more harm than goodand.
Opioids are powerful painkillers that have the potential to be addictive, so they are used as a last resort - for very severe pain.
Slow-acting drugs for osteoarthritis are agents that bring gradual but more lasting improvement. This group includesand:
- hyaluronic acid, .
- glucosamine, .
- chondroitin, .
- diacerein, .
These substances can be administered orally or by injection - straight into the joint. Studies conducted between 2001 and 2005 and in 2006 showed the effectiveness of these agents in slowing the progression of the disease and reducing painand.
Insoles and orthoses
.Did you know that the right knee orthoses can also reduce pain and facilitate movement? And on top of that... they don't have to be on the knee at all! Those recommended for gonarthrosis often come in the form of shoe inserts that increase cushioning when walking and change the position of the foot, which translates into the axis of the limb and the pressure exerted on the jointand.
The latest treatments for knee osteoarthritis
.
One of the latest treatments for gonarthrosis is prolotherapy using stem cells, taken from the patient's blood. Prolotherapy is a method that involves injecting the affected area (in this case the knee joint)and.
Till now, however, the evidence for the effectiveness of this therapy is not consistent. A 2020 study asked 257 people with gonarthrosis treated with various methods (including stem cell injections and platelet-rich plasma) which they considered to be most effective. Stem cell prolotherapy was chosen by 25% of respondentsand.
In contrast, a review of 2023 studies indicates that, while the use of stem cells reduces pain, it has no effect on improving knee function. Furthermore, this therapy is not at all free of side effectsand.
However, prolotherapy is not only about stem cells and platelet-rich plasma. It can also make use of other solutions, administered by injection.
A 2014 research paper described the case of a 72-year-old woman with grade 4 osteoarthritis in her knee, as observed on radiography. The woman was not eligible for knee replacement due to comorbidities.
Six sessions of prolotherapy with a dextrose-based solution and lidocaine were administered. After one year, radiographic imaging showed significant improvement in the joint, which this time showed only grade 1 degenerative changes .
It is worth mentioning, however, that this is only a description of one case, and in the course of treatment the patient was also recommended weight loss and physiotherapy .
.
Does diet have an effect on gonarthrosis?
.
One important factor in the treatment of knee osteoarthrosis is to maintain a normal body weight, or to lose it if you are obese . This relieves pressure on the knee joint and thus reduces the intensity of symptoms and slows the progression of degeneration.
A 2021 study indicated that the so-called Western diet, a diet based on processed foods rich in trans fats and simple sugars, is associated with an increased risk of developing knee degeneration. Not only is such a diet pro-inflammatory, it also makes it more likely to be overweight and obeseand.
A 2018 review of studies looked at the impact of the Mediterranean diet (considered the healthiest) on knee osteoarthritis. Although the conclusions are not conclusive, a positive effect of this diet on symptoms and the risk of gonarthrosisand was noted.
It is worth noting that the Mediterranean diet is rich in fish, and therefore in omega-3 acids. They exhibit anti-inflammatory properties and are recommended especially for frequently recurring or chronic inflammation.
Product description
The dietary supplement contains omega-3ᵀᴳ, or omega-3 acids in the form of trójglyceridesów. Scientific studies suggest that this form of fatty acidsós up to 2 times better absorbed than the estersós present in many dietary supplements on the market. This means that you are assured of their effectiveness and of supplying yourself with valuable omega acids.
Fatty acids omega-3 are derived from wild anchovy oil. It is a rich source of healthy fats that are essential for the health of the cardiovascular, immune and nervous systems, as well as the proper function of vision, joints muscles.
Scientific research suggests that wild anchovies are a good source of healthy fats.
Scientific research also suggests that an adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acidsós protects against and supports the treatment of depression and anxiety disorders. In addition, omega-3s influence the hydration and appearance of the skinóry and support healthy sleep.
.
The formula contains a total of 750 mg of EPA+DHA acidsós, which is three times higher than the recommended minimum of 250 mg for the Polish population. Omega-3 TG Premium has studies indicating that its TOTOX is 9, which is a very good result.
Supplementation of omega-3 fatty acidsóis recommended for anyone who does not eat 1–2 portions (approximately 300 g) of oily fish per week. Children during growth, seniors, physically active people, vegans and vegetarians, as well as patients undergoing cardiovascular treatment and prevention of heart disease also have an increased need.
Pros and cons
The dietary supplement contains omega-3ᵀᴳ, or omega-3 acids in the form of trójglyceridesów. Scientific studies suggest that this form of fatty acidsós up to 2 times better absorbed than the estersós present in many dietary supplements on the market. This means that you are assured of their effectiveness and of supplying yourself with valuable omega acids.
Fatty acids omega-3 are derived from wild anchovy oil. It is a rich source of healthy fats that are essential for the health of the cardiovascular, immune and nervous systems, as well as the proper function of vision, joints muscles.
Scientific research suggests that wild anchovies are a good source of healthy fats.
Scientific research also suggests that an adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acidsós protects against and supports the treatment of depression and anxiety disorders. In addition, omega-3s influence the hydration and appearance of the skinóry and support healthy sleep.
.
The formula contains a total of 750 mg of EPA+DHA acidsós, which is three times higher than the recommended minimum of 250 mg for the Polish population. Omega-3 TG Premium has studies indicating that its TOTOX is 9, which is a very good result.
Supplementation of omega-3 fatty acidsóis recommended for anyone who does not eat 1–2 portions (approximately 300 g) of oily fish per week. Children during growth, seniors, physically active people, vegans and vegetarians, as well as patients undergoing cardiovascular treatment and prevention of heart disease also have an increased need.
Additional information
The dietary supplement contains omega-3ᵀᴳ, or omega-3 acids in the form of trójglyceridesów. Scientific studies suggest that this form of fatty acidsós up to 2 times better absorbed than the estersós present in many dietary supplements on the market. This means that you are assured of their effectiveness and of supplying yourself with valuable omega acids.
Fatty acids omega-3 are derived from wild anchovy oil. It is a rich source of healthy fats that are essential for the health of the cardiovascular, immune and nervous systems, as well as the proper function of vision, joints muscles.
Scientific research suggests that wild anchovies are a good source of healthy fats.
Scientific research also suggests that an adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acidsós protects against and supports the treatment of depression and anxiety disorders. In addition, omega-3s influence the hydration and appearance of the skinóry and support healthy sleep.
.
The formula contains a total of 750 mg of EPA+DHA acidsós, which is three times higher than the recommended minimum of 250 mg for the Polish population. Omega-3 TG Premium has studies indicating that its TOTOX is 9, which is a very good result.
Supplementation of omega-3 fatty acidsóis recommended for anyone who does not eat 1–2 portions (approximately 300 g) of oily fish per week. Children during growth, seniors, physically active people, vegans and vegetarians, as well as patients undergoing cardiovascular treatment and prevention of heart disease also have an increased need.
Expert opinion
The dietary supplement contains omega-3ᵀᴳ, or omega-3 acids in the form of trójglyceridesów. Scientific studies suggest that this form of fatty acidsós up to 2 times better absorbed than the estersós present in many dietary supplements on the market. This means that you are assured of their effectiveness and of supplying yourself with valuable omega acids.
Fatty acids omega-3 are derived from wild anchovy oil. It is a rich source of healthy fats that are essential for the health of the cardiovascular, immune and nervous systems, as well as the proper function of vision, joints muscles.
Scientific research suggests that wild anchovies are a good source of healthy fats.
Scientific research also suggests that an adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acidsós protects against and supports the treatment of depression and anxiety disorders. In addition, omega-3s influence the hydration and appearance of the skinóry and support healthy sleep.
.
The formula contains a total of 750 mg of EPA+DHA acidsós, which is three times higher than the recommended minimum of 250 mg for the Polish population. Omega-3 TG Premium has studies indicating that its TOTOX is 9, which is a very good result.
Supplementation of omega-3 fatty acidsóis recommended for anyone who does not eat 1–2 portions (approximately 300 g) of oily fish per week. Children during growth, seniors, physically active people, vegans and vegetarians, as well as patients undergoing cardiovascular treatment and prevention of heart disease also have an increased need.
Product description
The dietary supplement contains high-quality fatty acids omega-3 from anchovy oil. It is a naturally rich source of healthy fats that are essential for cardiovascular, immune and nervous system health, as well as proper function of eyesight, joints muscles.
Scientific research also suggests that an adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acidsós protects against and supports the treatment of depression and anxiety disorders. In addition, omega-3s influence the hydration and appearance of the skinóry and support healthy sleep.
.
The dietary supplement contains 550 mg EPA+DHA per daily serving. This is more than double the official recommendations for the Polish population, whichóre suggesting an intake of at least 250 mg per day.
Supplementation of EPA+DHA is a good way to support healthy sleep.
Supplementation with omega-3 fatty acidsós is advisable if you do not consume 1–2 portions (approx. 300 g) of oily fish per week. There is also an increased need for physically active people, vegans and vegetarians, seniors, children during growth spurts and patients undergoing cardiovascular treatment and prevention of heart disease.
Pros and cons
The dietary supplement contains high-quality fatty acids omega-3 from anchovy oil. It is a naturally rich source of healthy fats that are essential for cardiovascular, immune and nervous system health, as well as proper function of eyesight, joints muscles.
Scientific research also suggests that an adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acidsós protects against and supports the treatment of depression and anxiety disorders. In addition, omega-3s influence the hydration and appearance of the skinóry and support healthy sleep.
.
The dietary supplement contains 550 mg EPA+DHA per daily serving. This is more than double the official recommendations for the Polish population, whichóre suggesting an intake of at least 250 mg per day.
Supplementation of EPA+DHA is a good way to support healthy sleep.
Supplementation with omega-3 fatty acidsós is advisable if you do not consume 1–2 portions (approx. 300 g) of oily fish per week. There is also an increased need for physically active people, vegans and vegetarians, seniors, children during growth spurts and patients undergoing cardiovascular treatment and prevention of heart disease.
Additional information
The dietary supplement contains high-quality fatty acids omega-3 from anchovy oil. It is a naturally rich source of healthy fats that are essential for cardiovascular, immune and nervous system health, as well as proper function of eyesight, joints muscles.
Scientific research also suggests that an adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acidsós protects against and supports the treatment of depression and anxiety disorders. In addition, omega-3s influence the hydration and appearance of the skinóry and support healthy sleep.
.
The dietary supplement contains 550 mg EPA+DHA per daily serving. This is more than double the official recommendations for the Polish population, whichóre suggesting an intake of at least 250 mg per day.
Supplementation of EPA+DHA is a good way to support healthy sleep.
Supplementation with omega-3 fatty acidsós is advisable if you do not consume 1–2 portions (approx. 300 g) of oily fish per week. There is also an increased need for physically active people, vegans and vegetarians, seniors, children during growth spurts and patients undergoing cardiovascular treatment and prevention of heart disease.
Expert opinion
The dietary supplement contains high-quality fatty acids omega-3 from anchovy oil. It is a naturally rich source of healthy fats that are essential for cardiovascular, immune and nervous system health, as well as proper function of eyesight, joints muscles.
Scientific research also suggests that an adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acidsós protects against and supports the treatment of depression and anxiety disorders. In addition, omega-3s influence the hydration and appearance of the skinóry and support healthy sleep.
.
The dietary supplement contains 550 mg EPA+DHA per daily serving. This is more than double the official recommendations for the Polish population, whichóre suggesting an intake of at least 250 mg per day.
Supplementation of EPA+DHA is a good way to support healthy sleep.
Supplementation with omega-3 fatty acidsós is advisable if you do not consume 1–2 portions (approx. 300 g) of oily fish per week. There is also an increased need for physically active people, vegans and vegetarians, seniors, children during growth spurts and patients undergoing cardiovascular treatment and prevention of heart disease.
Collagen for gonarthrosis
.
Collagen is a key component of cartilage tissue in joints, and research suggests that its supplementation may benefit those suffering from knee osteoarthritisand.
You may want to consider taking collagen dietary supplement to help with the symptoms of gonarthrosis, but more importantly to prevent its development. Choose hydrolysed collagen, which is more easily absorbed by the body, in a daily serving of 5-10g.
Natu.Care Collagen Premium 10000 mg, cherry

- Collagen content: 10,000 mg of hydrolyzed bovine collagen
- Additional active ingredients: vitamin C, low molecular weight hyaluronic acid, glucosamine, chondroitin, extract of Indian frankincense resin (boswellia serrata)
- Form: powder sachets for drinking
- Serving: 1 sachet per day
- Lasts for: 30 days
Product description
One of the strongest collagens on the market, providing as much as 10,000 mg per daily serving. This product can effectively support the condition of joints, skin, hair, and nails.
With this supplement, you will support your skeletal and joint system as well as your beauty, helping you visually halt the aging process and feel rejuvenated!
Pros and cons
Pros:
- The daily portion of collagen is very large – as much as 10,000 mg.
- Proven collagen formula – COLLinstant, whose effectiveness has been confirmed in clinical studies.
- Effective dose of hyaluronic acid, which additionally moisturizes the skin and positively affects joint health.
- Vitamin C supports the body's natural collagen production.
- Glucosamine is a fundamental building block of compounds found in joint cartilage and a component of collagen that gives elasticity to connective tissue in tendons.
- Chondroitin is a natural component found in the human body, mainly in cartilage. This large molecule (mucopolysaccharide) has the ability to absorb water, which helps maintain the elasticity and resilience of cartilage.
- Frankincense resin extract supports blood circulation and joint mobility and reduces their stiffness. It may help alleviate inflammatory conditions.
- The composition has been tested by the independent and accredited J.S. Hamilton laboratory.
Cons:
- None.
Additional information
Users praise Natu.Care Collagen Premium for the easy dissolving of the powder.
Natu.Care Premium collagen 10 000 mg, mango-maracuja

- Collagen content: 10,000 mg marine collagen hydrolysate
- Additional active ingredients: vitamin C, low molecular weight hyaluronic acid (and L-theanine and coenzyme Q10 in cocoa flavoured collagen or vitamin A and vitamin E in mango–passion fruit flavoured collagen)
- Form: powder sachets
- Dose: 1 sachet per day
- Sufficient for: 30 days
Product description
One of the strongest collagens on the market, whichós provides as much as 10,000 mg in a daily serving. This allows the formula to effectively support the condition of the skin, hair and nails.
With this supplement, you will support your beauty, which will allow you to visually stop the ageing process and feel a second youth!
Natu.Care Collagen Premium 10 000 mg comes in two flavours – cherry and mango-maracuja. Both formulas have the same product backbone – collagen, hyaluronic acid and vitamin C.
In the cherry version you additionally find glucosamine, chondroitin and Indian frankincense resin extract. Mango-maracuja, on the other hand, contains vitamin E and vitamin A.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Tested collagen formula – SeaGarden, whose effects have been confirmed in clinical studies.
- Effective dose of hyaluronic acid, additionally moisturizing the skin and positively impacting joint health.
- Vitamin C supports the body’s natural collagen production.
- The composition has been tested by the independent and accredited J.S. Hamilton laboratory.
- The product has an MSC (Marine Stewardship Council) quality certification – the collagen source supports sustainable fishing practices.
Cons:
- None.
Additional information
Users praise Natu.Care Collagen Premium for the easy dissolvability of the powder.
User review
I noticed a significant improvement in my skin texture after a few weeks of taking collagen regularly. My complexion is now as soft as velvet!
It is worth emphasising, however, that collagen supplementation will not replace either orthopaedic treatment or other aspects of managing knee osteoarthritis, such as maintaining a healthy body weight and regular physical activity. Taking collagen should be considered as an adjunct to these strategies.

Sprawdź, za co pokochały go tysiące klientek Natu.Care Premium Omega-3ᵀᴳ -15% z kodem BLOG15
Natu.Care Omega-3ᵀᴳ Premium
Natu.Care Omega-3ᵀᴳ Premium dla zdrowia serca, mózgu i odporności. Najlepsza przyswajalność. Optymalna dawka 750 mg. Przebadana przez niezależne laboratorium.
Zobacz więcej
Produkt ma super skład, transparentną etykietę i co dla mnie jest ważne – małe kapsułki do połknięcia. Nie ma też nieprzyjemnego efektu odbijania rybą, który miałam spożywając inne produkty. Widzę znaczną poprawę odporności. Polecam!@Kasia P.
Summary
.
- Gonarthrosis is a degenerative disease of the knee joint. .
- In its course, the articular cartilage degrades and the bones begin to rub against each other. .
- As a result, osteophytes form on the surface of the bones and the joint crevices atrophy. .
- Symptoms of gonarthrosis include knee pain, stiffness and limited mobility. Recurrent inflammation and swelling may also occur.
- Treatment.
- Treatment of gonarthrosis of the knee depends on the severity of the condition. The most common initial treatments are pharmacotherapy aimed at managing pain and inflammation and physiotherapy. Special orthotics and orthoses may also be helpful. .
- In advanced stages of gonarthrosis, surgical procedures are used. These include arthroscopic debridement of the joint and the implantation of a partial or total endoprosthesis.
- The following treatments are available.
- A nutritious and balanced diet can reduce the risk of gonarthrosis, as well as support the management of its symptoms.
FAQ
.What does knee osteoarthritis look like?
.Knee osteoarthritis, also known as gonarthrosis, is a chronic disease associated with degeneration of the articular cartilage. It manifests as pain, loss of mobility and deformity of the joint.
On imaging examination (usually X-ray), a specialist may note the appearance of osteophytes, which are lumps and growths on the surface of the bones that make up the joint. The spaces visible between them (joint crevices), i.e. the areas where cartilage and joint fluid are normally located, also diminish.
The joint crevices are also reduced.
What does primary bilateral gonarthrosis mean?
.Primary bilateral gonarthrosis is the medical term for degeneration of both knee joints. The disease is characterised by degradation of the articular cartilage, whereby the structures of the joint and the bones that connect it are destroyed.
Is it possible to ride a bicycle with gonarthrosis?
.Yes, cycling is possible with gonarthrosis, provided there is no active inflammation going on in the knee joint. Cycling strengthens the quadriceps muscles in the thighs, which stabilise and relieve pressure on the knee joints. This may help to slow the progression of the condition and reduce knee pain.
Is gonarthrosis treatable?
.No, gonarthrosis, or degeneration of the knee joint, is not curable. However, appropriately selected orthopaedic treatment, combined with physiotherapy, can reduce symptoms such as joint stiffness, limited mobility and pain.
The following is an example.
In the case of very advanced gonarthrosis, a knee replacement may also be used. Such a procedure is aimed at restoring function to the patient.
The patient's knee can be replaced with an endoprosthesis.
How does gonarthrosis hurt?
.Gonarthrosis, or degeneration of the knee joint, causes knee pain of varying severity and nature. Most often it is a dull, pressing pain that is worse during movement or prolonged standing. There may also be sharp pain during sudden movements. The pain is often worse after a period of inactivity, such as sitting.
What helps knee osteoarthritis?
.Lower the load on the knee joint. If you suffer from obesity, try to reduce your body weight, as every extra kilogram increases the pressure on your joints.
Exercise regularly. Choose low-intensity forms of activity, such as swimming or cycling, which improve muscle strength and joint mobility.
Even if you are suffering from a joint strain, try to exercise regularly.
If the pain worsens, you can use painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. Remember, however, that the cornerstone of treatment for knee osteoarthritis is appropriate therapy under the guidance of an orthopaedic surgeon and physiotherapy.
Is it possible to walk a lot with knee osteoarthritis?
.Moderate physical activity is recommended for knee osteoarthritis. Walking is good, but don't overdo it. Choose to walk on flat ground and avoid steep hills and stairs.
Incorporate muscle-strengthening exercises into your routine, such as leg extensions with a light load. These exercises help to stabilise the knee joint, which can reduce pain and improve mobility.
Attend to the following exercises.
Follow the recommendations of your doctor and physiotherapist. If necessary, use orthopaedic aids such as orthoses and special shoe inserts.
Follow the advice of your doctor and physiotherapist.
.
Resources
.See all
.Altuwairqi, A. A., Qronfla, H. M., Aljehani, L. S., & Khashoggi, K. G. (2023). The Association Between Gonarthrosis Pain Severity and Radiographic Findings on X-Ray: A Cross-Sectional Study. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.35258
Altuwairqi, A. A., Qronfla, H. M., Aljehani, L. S., Khashoggi, K. G., Altuwairqi, A., Qronfla, H. M., Aljehani, L. S., & Khashoggi, K. (2023). The Association Between Gonarthrosis Pain Severity and Radiographic Findings on X-Ray: A Cross-Sectional Study. Cureus, 15(2). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.35258
Ärzteblatt, D. Ä. G., Redaktion Deutsches. (n.d.). The Epidemiology, Etiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Osteoarthritis of the Knee (05.03.2010). Deutsches Ärzteblatt. Retrieved December 13, 2023, from https://www.aerzteblatt.de/int/archive/article?id=68000
Netter's Atlas of Orthopaedic Anatomy. (n.d.). PZWL Medical Bookshop. Retrieved December 7, 2023, from https://pzwl.pl/Atlas-anatomii-ortopedycznej-Nettera,5041703,p.html
Bruyère, O., Honvo, G., Veronese, N., Arden, N. K., Branco, J., Curtis, E. M., Al-Daghri, N. M., Herrero-Beaumont, G., Martel-Pelletier, J., Pelletier, J.-P., Rannou, F., Rizzoli, R., Roth, R., Uebelhart, D., Cooper, C., & Reginster, J.-Y. (2019). An updated algorithm recommendation for the management of knee osteoarthritis from the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Diseases (ESCEO). Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism, 49(3), 337-350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2019.04.008
Campbell Orthopaedic Surgery Volume 1, S. Terry Canale, James H. Beaty. (n.d.). MediPage Medical Publishing. Retrieved December 7, 2023, from https://medipage.pl/pl/p/Campbell-Ortopedia-Operacyjna-TOM-1%2C-S.-Terry-Canale%2C-James-H.-Beaty/2774
Chitnavis, J., Sinsheimer, J. S., Suchard, M. A., Clipsham, K., & Carr, A. J. (2000). End-stage coxarthrosis and gonarthrosis. Aetiology, clinical patterns and radiological features of idiopathic osteoarthritis. Rheumatology, 39(6), 612-619. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/39.6.612
Hannan, M. T., Felson, D. T., & Pincus, T. (2000). Analysis of the discordance between radiographic changes and knee pain in osteoarthritis of the knee. The Journal of Rheumatology, 27(6), 1513-1517.
Kubsik-Gidlewska, A., Klupinski, K., Krochmalski, M., Krochmalski, J., Klimkiewicz, P., Woldańska-Okońska, M., & Ska, M. (2018). CD34+ stem cell treatment for knee osteoarthritis: A treatment and rehabilitation algorithm. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine - Clinical Communications, 1, 1-6. https://doi.org/10.2340/20030711-1000012
Surgical treatment in osteoarthritis. Schnettler, Steinau. (n.d.). MediPage Medical Publishing. Retrieved December 7, 2023, from https://medipage.pl/pl/p/Leczenie-chirurgiczne-w-zapaleniach-kosci-i-stawow.-Schnettler%2C-Steinau/1991
Loria, M. P., Dambra, P., Moretti, B., Patella, V., Capuzzimati, L., Cavallo, E., Nettis, E., Pesce, V., Dell'Osso, A., Simone, C., & Tursi, A. (2004). Role of cytokines in gonarthrosis and knee prosthesis aseptic loosening. Journal of Orthopaedic Science, 9(3), 274-279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-004-0774-7
Macri, E. M., Runhaar, J., Damen, J., Oei, E. H. G., & Bierma-Zeinstra, S. M. A. (2022). Kellgren/Lawrence Grading in Cohort Studies: Methodological Update and Implications Illustrated Using Data From a Dutch Hip and Knee Cohort. Arthritis Care & Research, 74(7), 1179-1187. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.24563
Morales-Ivorra, I., Romera-Baures, M., Roman-Viñas, B., & Serra-Majem, L. (2018). Osteoarthritis and the Mediterranean Diet: A Systematic Review. Nutrients, 10(8), Article 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10081030
Moseley, J. B., O'Malley, K., Petersen, N. J., Menke, T. J., Brody, B. A., Kuykendall, D. H., Hollingsworth, J. C., Ashton, C. M., & Wray, N. P. (2002). A Controlled Trial of Arthroscopic Surgery for Osteoarthritis of the Knee. New England Journal of Medicine, 347(2), 81-88. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa013259
Nahhas, C. R., Fuller, B. C., Hannon, C. P., Gerlinger, T. L., Nam, D., & Della Valle, C. J. (2020). Which Nonsurgical Treatments Do Patients Believe Are Most Effective for Hip and Knee Arthritis? JAAOS Global Research & Reviews, 4(5), e20.00046. https://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-20-00046
Noël, E., & Nissen, M. J. (2008). The medical treatment of gonarthrosis. IN M. Bonnin & P. Chambat (Ed.), Osteoarthritis of the knee (pp. 59-68). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-2-287-74175-3_4
Orthopaedics and Traumatology Volume 1-2. (n.d.). PZWL Medical Bookshop. Retrieved December 7, 2023, from https://pzwl.pl/Ortopedia-i-traumatologia-Tom-1-2,4964653,p.html
Petrella, R. J., & Petrella, M. (2006). A prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy of intraarticular hyaluronic acid for osteoarthritis of the knee. The Journal of Rheumatology, 33(5), 951-956.
Book for doctors specialising in orthopaedics and traumatology of the musculoskeletal system-Andrzej Nowakowski,Łukasz Matuszewski,Marek Synder,Tomasz Mazurek. (n.d.). Retrieved December 7, 2023, from https://www.medicon.pl/podrecznik-dla-doctors-specialising-in-orthopaedics-and-traumatology-motor-access/32341?gad_source=1&gclid=CjwKCAiA98WrBhAYEiwA2WvhOi5tRhqM4RWQnJul5WXDlcJg99iCzfC-CW45kTG0oRxccPpaK3YveRoCqxoQAvD_BwE
Ries, M. D., Philbin, E. F., & Groff, G. D. (1995). Relationship Between Severity of Gonarthrosis and Cardiovascular Fitness. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research®, 313, 169.
Shang, Z., Wanyan, P., Zhang, B., Wang, M., & Wang, X. (2023). A systematic review, umbrella review, and quality assessment on clinical translation of stem cell therapy for knee osteoarthritis: Are we there yet? Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 14(1), 91. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-023-03332-5
Snelling, S., Rout, R., Davidson, R., Clark, I., Carr, A., Hulley, P. A., & Price, A. J. (2014). A gene expression study of normal and damaged cartilage in anteromedial gonarthrosis, a phenotype of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, 22(2), 334-343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2013.12.009
Solmaz, I., Deniz, S., & Cifci, O. T. (2014). Treatment of Advanced Stage Gonarthrosis With Prolotherapy: Case Report. Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, 4(1), Article 1. https://doi.org/10.5812/aapm.9171
Towheed, T., Maxwell, L., Anastassiades, T. P., Shea, B., Houpt, J. B., Welch, V., Hochberg, M. C., & Wells, G. A. (2005). Glucosamine therapy for treating osteoarthritis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD002946.pub2
Traumatology of the musculoskeletal system. (n.d.). PZWL Medical Bookshop. Retrieved December 7, 2023, from https://pzwl.pl/Traumatologia-ukladu-ruchu,4985755,p.html
Xu, C., Liu, T., Driban, J. B., McAlindon, T., Eaton, C. B., & Lu, B. (2021). Dietary patterns and risk of developing knee osteoarthritis: Data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, 29(6), 834-840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2021.02.571
..
Editorials
Meet the team



Chondroitin helps the joints and other elements of the body.

Glutathione is one of the most potent antioxidants for supporting the body's health. Find out how it works and where to get it from.

See why hip joints hurt and how to treat their ailments.


