- Home
- Omega acids
Omega fatty acids (what they are, what they are in and what they help)
Find out why health-promoting omega acids should be on your plate every day.


Learn more about our editorial process
.

Learn more about our editorial process
.

Learn more about our editorial process
.

Learn more about our editorial process
.
Why you can trust us
Articles on Natu.Care are written based on scientific research, data from government websites and other reliable sources. The texts are written in cooperation with doctors, nutritionists and other health and beauty experts. Articles are reviewed before publication and during significant updates.
.Learn more about our editorial process
.Information about advertisements
Content on Natu.Care may contain links to products from the sale of which we may receive a commission. When creating content, we adhere to high editorial standards and take care to be objective about the products discussed. The presence of affiliate links is not dictated by our partners, and we select the products we review ourselves completely independently.
.Learn more about our terms and Conditions
.Omega acids are such a royal family in the world of fatty acids. Encased in golden capsules, they are admired, desired but not fully understood. From the outside, we don't see their relationships and conflicts as from 'The Crown'.
You are not aware of the drama going on in your bloodstream even at this moment. A fierce battle in the fatty ring for space in your body and a wrestling match between plant sources and fish sources. The only way to calm the situation is... to turn 'Game of Thrones' into 'House on the Prairie'.
Learn what to do to get the most out of them for your health and stop them from massacring each other.
Prepare your popcorn (in oil - you'll understand why soon enough) and see what goes on behind the scenes -
From this article you will learn:
- What omega acids exist and what they do .
- What omega acids give you .
- How to get the most out of your omega-3 to omega-6 ratio .
- How to eat to provide the right acids in the ideal ratio .
- Why omega 3-6-9 supplements are a bad idea .

Sprawdź, za co pokochały go tysiące klientek Natu.Care Premium Omega-3ᵀᴳ -15% z kodem BLOG15
Natu.Care Omega-3ᵀᴳ Premium
Natu.Care Omega-3ᵀᴳ Premium dla zdrowia serca, mózgu i odporności. Najlepsza przyswajalność. Optymalna dawka 750 mg. Przebadana przez niezależne laboratorium.
Zobacz więcej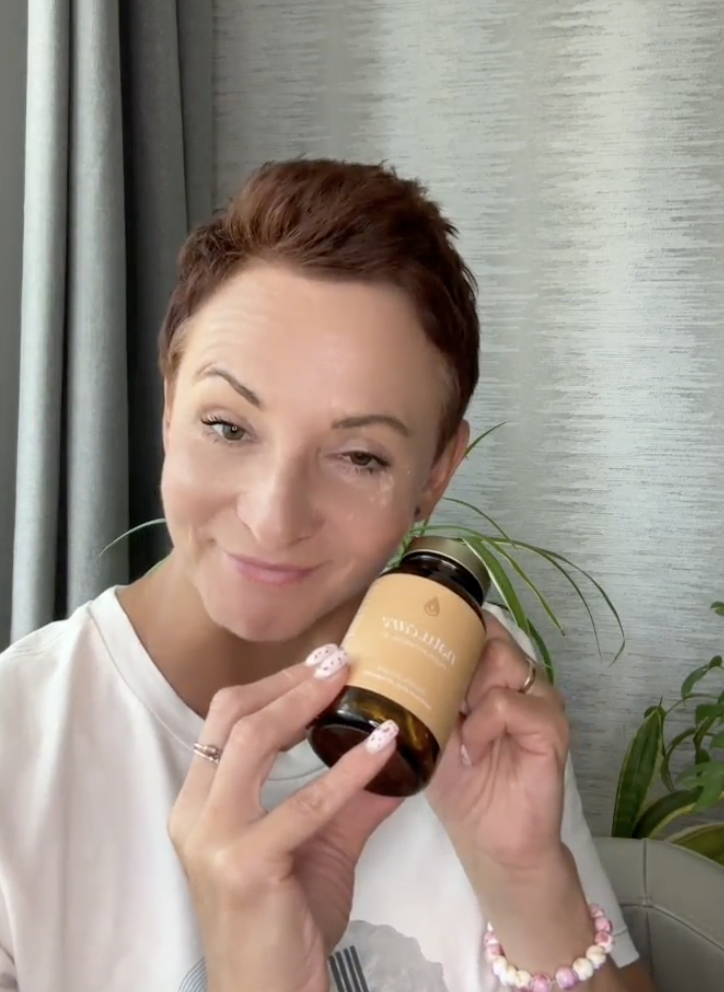
Produkt ma super skład, transparentną etykietę i co dla mnie jest ważne – małe kapsułki do połknięcia. Nie ma też nieprzyjemnego efektu odbijania rybą, który miałam spożywając inne produkty. Widzę znaczną poprawę odporności. Polecam!@Kasia P.
See also:
.- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Omega-6 fatty acids
- Omega-9 fatty acids
- Omega 3-6-9 acids .
- Deficiency of omega-3 fatty acids .
- Omega-3 medicine, not a supplement .
- EPA acid
- DHA acid .
- ALA acid
- Tran
Omega acids - types and breakdown
.What are omega acids?
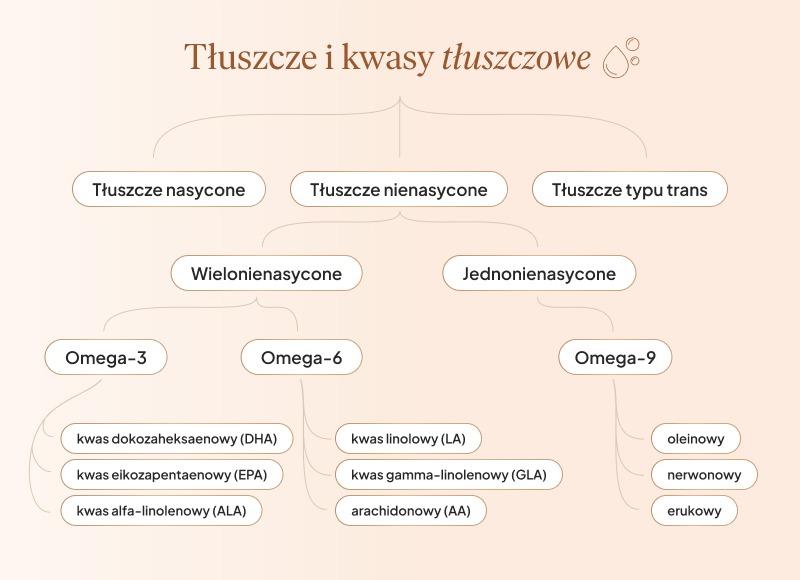
.Omeega acids belong to the group of fatty acidsand of which there are three types: saturated, unsaturated, trans.
.Fatty acids are needed for energy production, building cell membranes, hormone and neurotransmitter production. They are essential for the proper functioning of the nervous, cardiovascular and immune systems. Most important for our bodies are unsaturated acids - which include omega 3, 6, 7 and 9and.
Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids must be provided with diet or supplementation. In contrast, omega-5, omega-7 and omega-9 acids are naturally produced by the body..
 .
.
Julia SkrajdaDietitian
.Important
Green unsaturated fatty acids PUFA (polyunsaturated fatty acids) and monounsaturated fatty acids MUFA (monounsaturated fatty acids) are essential 'good fats' that are responsible for many important processes in our bodies, such as brain development, protection against heart disease or improving skin and hair condition.
There is also another way of writing these acids, where instead of omega there is the letter n. So, for example, omega-3 acid is n-3, omega-6 is n-6.
Product description
The dietary supplement contains omega-3ᵀᴳ, or omega-3 acids in the form of trójglyceridesów. Scientific studies suggest that this form of fatty acidsós up to 2 times better absorbed than the estersós present in many dietary supplements on the market. This means that you are assured of their effectiveness and of supplying yourself with valuable omega acids.
Fatty acids omega-3 are derived from wild anchovy oil. It is a rich source of healthy fats that are essential for the health of the cardiovascular, immune and nervous systems, as well as the proper function of vision, joints muscles.
Scientific research suggests that wild anchovies are a good source of healthy fats.
Scientific research also suggests that an adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acidsós protects against and supports the treatment of depression and anxiety disorders. In addition, omega-3s influence the hydration and appearance of the skinóry and support healthy sleep.
.
The formula contains a total of 750 mg of EPA+DHA acidsós, which is three times higher than the recommended minimum of 250 mg for the Polish population. Omega-3 TG Premium has studies indicating that its TOTOX is 9, which is a very good result.
Supplementation of omega-3 fatty acidsóis recommended for anyone who does not eat 1–2 portions (approximately 300 g) of oily fish per week. Children during growth, seniors, physically active people, vegans and vegetarians, as well as patients undergoing cardiovascular treatment and prevention of heart disease also have an increased need.
Pros and cons
The dietary supplement contains omega-3ᵀᴳ, or omega-3 acids in the form of trójglyceridesów. Scientific studies suggest that this form of fatty acidsós up to 2 times better absorbed than the estersós present in many dietary supplements on the market. This means that you are assured of their effectiveness and of supplying yourself with valuable omega acids.
Fatty acids omega-3 are derived from wild anchovy oil. It is a rich source of healthy fats that are essential for the health of the cardiovascular, immune and nervous systems, as well as the proper function of vision, joints muscles.
Scientific research suggests that wild anchovies are a good source of healthy fats.
Scientific research also suggests that an adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acidsós protects against and supports the treatment of depression and anxiety disorders. In addition, omega-3s influence the hydration and appearance of the skinóry and support healthy sleep.
.
The formula contains a total of 750 mg of EPA+DHA acidsós, which is three times higher than the recommended minimum of 250 mg for the Polish population. Omega-3 TG Premium has studies indicating that its TOTOX is 9, which is a very good result.
Supplementation of omega-3 fatty acidsóis recommended for anyone who does not eat 1–2 portions (approximately 300 g) of oily fish per week. Children during growth, seniors, physically active people, vegans and vegetarians, as well as patients undergoing cardiovascular treatment and prevention of heart disease also have an increased need.
Additional information
The dietary supplement contains omega-3ᵀᴳ, or omega-3 acids in the form of trójglyceridesów. Scientific studies suggest that this form of fatty acidsós up to 2 times better absorbed than the estersós present in many dietary supplements on the market. This means that you are assured of their effectiveness and of supplying yourself with valuable omega acids.
Fatty acids omega-3 are derived from wild anchovy oil. It is a rich source of healthy fats that are essential for the health of the cardiovascular, immune and nervous systems, as well as the proper function of vision, joints muscles.
Scientific research suggests that wild anchovies are a good source of healthy fats.
Scientific research also suggests that an adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acidsós protects against and supports the treatment of depression and anxiety disorders. In addition, omega-3s influence the hydration and appearance of the skinóry and support healthy sleep.
.
The formula contains a total of 750 mg of EPA+DHA acidsós, which is three times higher than the recommended minimum of 250 mg for the Polish population. Omega-3 TG Premium has studies indicating that its TOTOX is 9, which is a very good result.
Supplementation of omega-3 fatty acidsóis recommended for anyone who does not eat 1–2 portions (approximately 300 g) of oily fish per week. Children during growth, seniors, physically active people, vegans and vegetarians, as well as patients undergoing cardiovascular treatment and prevention of heart disease also have an increased need.
Expert opinion
The dietary supplement contains omega-3ᵀᴳ, or omega-3 acids in the form of trójglyceridesów. Scientific studies suggest that this form of fatty acidsós up to 2 times better absorbed than the estersós present in many dietary supplements on the market. This means that you are assured of their effectiveness and of supplying yourself with valuable omega acids.
Fatty acids omega-3 are derived from wild anchovy oil. It is a rich source of healthy fats that are essential for the health of the cardiovascular, immune and nervous systems, as well as the proper function of vision, joints muscles.
Scientific research suggests that wild anchovies are a good source of healthy fats.
Scientific research also suggests that an adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acidsós protects against and supports the treatment of depression and anxiety disorders. In addition, omega-3s influence the hydration and appearance of the skinóry and support healthy sleep.
.
The formula contains a total of 750 mg of EPA+DHA acidsós, which is three times higher than the recommended minimum of 250 mg for the Polish population. Omega-3 TG Premium has studies indicating that its TOTOX is 9, which is a very good result.
Supplementation of omega-3 fatty acidsóis recommended for anyone who does not eat 1–2 portions (approximately 300 g) of oily fish per week. Children during growth, seniors, physically active people, vegans and vegetarians, as well as patients undergoing cardiovascular treatment and prevention of heart disease also have an increased need.
Product description
The dietary supplement contains high-quality fatty acids omega-3 from anchovy oil. It is a naturally rich source of healthy fats that are essential for cardiovascular, immune and nervous system health, as well as proper function of eyesight, joints muscles.
Scientific research also suggests that an adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acidsós protects against and supports the treatment of depression and anxiety disorders. In addition, omega-3s influence the hydration and appearance of the skinóry and support healthy sleep.
.
The dietary supplement contains 550 mg EPA+DHA per daily serving. This is more than double the official recommendations for the Polish population, whichóre suggesting an intake of at least 250 mg per day.
Supplementation of EPA+DHA is a good way to support healthy sleep.
Supplementation with omega-3 fatty acidsós is advisable if you do not consume 1–2 portions (approx. 300 g) of oily fish per week. There is also an increased need for physically active people, vegans and vegetarians, seniors, children during growth spurts and patients undergoing cardiovascular treatment and prevention of heart disease.
Pros and cons
The dietary supplement contains high-quality fatty acids omega-3 from anchovy oil. It is a naturally rich source of healthy fats that are essential for cardiovascular, immune and nervous system health, as well as proper function of eyesight, joints muscles.
Scientific research also suggests that an adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acidsós protects against and supports the treatment of depression and anxiety disorders. In addition, omega-3s influence the hydration and appearance of the skinóry and support healthy sleep.
.
The dietary supplement contains 550 mg EPA+DHA per daily serving. This is more than double the official recommendations for the Polish population, whichóre suggesting an intake of at least 250 mg per day.
Supplementation of EPA+DHA is a good way to support healthy sleep.
Supplementation with omega-3 fatty acidsós is advisable if you do not consume 1–2 portions (approx. 300 g) of oily fish per week. There is also an increased need for physically active people, vegans and vegetarians, seniors, children during growth spurts and patients undergoing cardiovascular treatment and prevention of heart disease.
Additional information
The dietary supplement contains high-quality fatty acids omega-3 from anchovy oil. It is a naturally rich source of healthy fats that are essential for cardiovascular, immune and nervous system health, as well as proper function of eyesight, joints muscles.
Scientific research also suggests that an adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acidsós protects against and supports the treatment of depression and anxiety disorders. In addition, omega-3s influence the hydration and appearance of the skinóry and support healthy sleep.
.
The dietary supplement contains 550 mg EPA+DHA per daily serving. This is more than double the official recommendations for the Polish population, whichóre suggesting an intake of at least 250 mg per day.
Supplementation of EPA+DHA is a good way to support healthy sleep.
Supplementation with omega-3 fatty acidsós is advisable if you do not consume 1–2 portions (approx. 300 g) of oily fish per week. There is also an increased need for physically active people, vegans and vegetarians, seniors, children during growth spurts and patients undergoing cardiovascular treatment and prevention of heart disease.
Expert opinion
The dietary supplement contains high-quality fatty acids omega-3 from anchovy oil. It is a naturally rich source of healthy fats that are essential for cardiovascular, immune and nervous system health, as well as proper function of eyesight, joints muscles.
Scientific research also suggests that an adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acidsós protects against and supports the treatment of depression and anxiety disorders. In addition, omega-3s influence the hydration and appearance of the skinóry and support healthy sleep.
.
The dietary supplement contains 550 mg EPA+DHA per daily serving. This is more than double the official recommendations for the Polish population, whichóre suggesting an intake of at least 250 mg per day.
Supplementation of EPA+DHA is a good way to support healthy sleep.
Supplementation with omega-3 fatty acidsós is advisable if you do not consume 1–2 portions (approx. 300 g) of oily fish per week. There is also an increased need for physically active people, vegans and vegetarians, seniors, children during growth spurts and patients undergoing cardiovascular treatment and prevention of heart disease.
ALLNUTRITION Omega 3 Strong

- Content omega-3 acids: 550 mg (DHA 220 mg + EPA 330 mg)
- Additional active ingredients: vitamin E
- Form: capsules .
- Dose: 1 capsule per day .
- Sufficient for: 90 days .
Product description
A dietary supplement with a solid portion of DHA and EPA – valuable for health and well-being omega-3 acidsós. Indicated especially for people on a plant-based diet, physically active people and seniors.
.The sourceóof omega-3 acids in this preparation is fish oil.
.Pros and cons
A dietary supplement with a solid portion of DHA and EPA – valuable for health and well-being omega-3 acidsós. Indicated especially for people on a plant-based diet, physically active people and seniors.
.The sourceóof omega-3 acids in this preparation is fish oil.
.Additional information
A dietary supplement with a solid portion of DHA and EPA – valuable for health and well-being omega-3 acidsós. Indicated especially for people on a plant-based diet, physically active people and seniors.
.The sourceóof omega-3 acids in this preparation is fish oil.
.User review
A dietary supplement with a solid portion of DHA and EPA – valuable for health and well-being omega-3 acidsós. Indicated especially for people on a plant-based diet, physically active people and seniors.
.The sourceóof omega-3 acids in this preparation is fish oil.
.Solgar Omega 3-6-9

- Content of omega acids:.
- Omega-3 fatty acids.
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) – 585 mg
.- eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) – 344 mg
- docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) – 221 mg
.
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Omega-6 fatty acids.
- linoleic acid (LA) – 598 mg .
- gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) – 274 mg .
- Omega-9 fatty acids.
- Oleic acid – 325 mg .
- Omega-3 fatty acids.
- Source of omega acids: fish oil from anchovies, mackerel, sardines, linseed oil, cucumber oil .
- Form: capsules .
- Packaging: 60 capsules .
- Daily allowance:3 capsules per day .
- Sufficient for: 20 days .
Product description
A combination of omega 3-6-9 fatty acidsós derived from fish and plants. The dietary supplement supplements essential omega fatty acids, whichóre needed for the proper functioning of many systemsóorgansóin the body.
Pros and cons
A combination of omega 3-6-9 fatty acidsós derived from fish and plants. The dietary supplement supplements essential omega fatty acids, whichóre needed for the proper functioning of many systemsóorgansóin the body.
Additional information
A combination of omega 3-6-9 fatty acidsós derived from fish and plants. The dietary supplement supplements essential omega fatty acids, whichóre needed for the proper functioning of many systemsóorgansóin the body.
A combination of omega 3-6-9 fatty acidsós derived from fish and plants. The dietary supplement supplements essential omega fatty acids, whichóre needed for the proper functioning of many systemsóorgansóin the body.
Omega + Vitamin D3 800 IU for children

- Content of omega-3 fatty acids: 300 mg (180 mg EPA + 120 mg DHA)
- .
- Additional active ingredients: vitamin D3
- Form: twist-off capsules
- .
- Dose: 1 capsule per day
- .
- Sufficient for: 60 days
- .
Product description
Omega-3 acids for children with added vitamin D3 in good doses. The formula fills the daily requirement of EPA and DHA and vitamin D for children aged 2–18 years.
The Ministry of Health recommends supplementation with vitamin D3. In turn, omega-3 fatty acids are also crucial for the youngest.
The dietary supplement from Aura Herbals supports mós brain function, proper vision and immune system function.
The omega-3 fatty acids are derived from fish oil sourced from anchovies.
Pros and cons
Omega-3 acids for children with added vitamin D3 in good doses. The formula fills the daily requirement of EPA and DHA and vitamin D for children aged 2–18 years.
The Ministry of Health recommends supplementation with vitamin D3. In turn, omega-3 fatty acids are also crucial for the youngest.
The dietary supplement from Aura Herbals supports mós brain function, proper vision and immune system function.
The omega-3 fatty acids are derived from fish oil sourced from anchovies.
Additional information
Omega-3 acids for children with added vitamin D3 in good doses. The formula fills the daily requirement of EPA and DHA and vitamin D for children aged 2–18 years.
The Ministry of Health recommends supplementation with vitamin D3. In turn, omega-3 fatty acids are also crucial for the youngest.
The dietary supplement from Aura Herbals supports mós brain function, proper vision and immune system function.
The omega-3 fatty acids are derived from fish oil sourced from anchovies.
User review
Omega-3 acids for children with added vitamin D3 in good doses. The formula fills the daily requirement of EPA and DHA and vitamin D for children aged 2–18 years.
The Ministry of Health recommends supplementation with vitamin D3. In turn, omega-3 fatty acids are also crucial for the youngest.
The dietary supplement from Aura Herbals supports mós brain function, proper vision and immune system function.
The omega-3 fatty acids are derived from fish oil sourced from anchovies.
Omega-3 fatty acids
.In a nutshell
Omega-3s are important DHA, EPA and ALA acids that support the nervous system, protect the heart, joints and eyes and take care of mental health. You can find the most omega-3s in oily fish, flaxseed oil and chia seeds. Deficiency can lead to problems with immunity, lack of energy, joints and even reduced mood.
Omega-3 fatty acids are the polyunsaturated fatty acids you need to get from your diet (not just a diet full of fish) or supplementationand.
The most important omega-3 fatty acids areand:
.- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA): produces eicosanoids, which help reduce inflammation in the body, .
- docosahexaenoic acid (DHA): crucial for brain development and function, .
- alpha-linolenic acid (ALA): involved in the production of EPA and DHA, supports the heart and nervous system.
Properties of omega-3 fatty acids
.Omega-3 fatty acids take care of:
.- the brain and nervous system,
- heart and circulatory system, .
- muscles, joints and bones, .
- vision, .
- mental health, .
- skin, hair and nail health,
- sleep and regeneration.
- sleep and regeneration, .
- pain and stiffness in the joints, .
- dry eyes, .
- dryness of the skin, .
- irritation, .
- acne, .
- hair loss, .
- lower mood and anxiety, .
- decreased blood clotting, .
- nose bleeding, .
- diarrhoea, flatulence, belching, nausea, .
- reflux, .
- increased blood sugar, .
- reduction of blood pressure,
- reduction of blood pressure.
- increased insomnia or anxiety, .
- linoleic acid (LA), .
- gamma-linolenic acid (GLA), .
- arachidonic acid (AA), .
- heart and cardiovascular system,
- brain and nervous system, .
- metabolism, .
- control of inflammation, .
- skin, .
- dry and flaky skin, .
- impaired wound healing, .
- increased susceptibility to skin infections, .
- deterioration in concentration and sustaining attention,
- deterioration in concentration and sustaining attention.
- mood disorders such as depression and irritability, .
- increased risk of heart disease and other chronic diseases, .
- disorders of growth and development in children, .
- hormonal disorders, .
- disruption of inflammatory processes in the body, .
- deterioration of joint condition and increased risk of rheumatic diseases, .
- joint inflammation and pain, .
- skin lesions, e.g. pustoriasis, acne, .
- hormonal disorders, .
- immune disorders, .
- heart and cardiovascular system,
- brain and nervous system, .
- sugar and insulin metabolism, .
- psychology and mood, .
- inflammation control, .
- skin, .
- disorders of lipid metabolism and insulin resistance, .
- deterioration of blood lipid profile, .
- dysfunction of the nervous system, .
- deterioration of the intestinal barrier function, .
- increased risk of heart disease, .
- deterioration of the skin (dryness, irritation, acne), .
- increase in body weight, .
- development of metabolic diseases, e.g. insulin resistance, type II diabetes, .
- increased risk of heart disease and cancerand.
- 5 g mackerel, .
- 7 g salmon, .
- 4 g trout, .
- 2 tablespoons flaxseed oil, rapeseed oil or olive oil, .
- a handful of walnuts, .
- Regularly eat fish, e.g. salmon, tuna, mackerel, herring.
- Eat fish regularly.
- Avoid highly processed foods, e.g. convenience foods, sweets, snacks.
- Avoid highly processed foods, e.g. convenience foods, sweets, snacks.
- Don't stress about the ratio of omega-3 and omega-6 in each food.
- Persons who are unable to provide adequate amounts of these fats from food.
- Persons who are unable to provide adequate amounts of these fats from food.
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women.
- Pregnant women and breastfeeding women.
- Children during periods of intensive growth. .
- Seniors. .
- Patients receiving cardiac treatment and prevention of heart disease. .
- Patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis. .
- Allergic patients. .
- People who are very physically active. .
- Capsules with omega-3 have a longer shelf life. Their airtight seal ensures that the oil is not exposed to air, which prolongs its quality. As a result, such preparations are free of unnecessary chemicals - preservatives or antioxidants.
- The liquid form has a shorter shelf life once opened - about 30 days. You generally need to store the bottle in the fridge.
- Take advantage of promotions. Browse offers such as multi-packs, multi-packs, or 2+1.
- Freeze products. In the freezer, you can keep not only fish, but also nuts or vegetables.
- Use price comparison apps. I was surprised when I started comparing prices in different shops - the differences of the same product were up to £8. .
- Take care with food storage. Read up on how to store foods properly and enjoy their freshness for longer, e.g. pack nuts in airtight containers, buy oils in dark bottles and keep avocados in water.
- Clean up your food.
- Buy seasonally. Prices of some products depend on weather conditions, harvest or fishing. E.g. salmon and almonds record the lowest prices in summer, walnut is cheapest in autumn.
- Hypersensitivity to any ingredient in the formulation, .
- sensitivity to fish or shellfish, .
- blood clotting disorders (e.g. haemophilia), .
- has a history of heart attack or ischaemic stroke, .
- taking anticoagulant medication (e.g. aspirin, warfarin), .
- chronic kidney disease or liver disease, .
- taking oral anti-diabetic medicationand. .
- The omega acids we need to provide with our food are omega-3 and 6.
- Ideal ratio of omega-3 to omega-6.
- The ideal ratio of omega-3 to 6 acids should be between 1:1 and 1:4. .
- The modern diet provides an unhealthy ratio because omega-6 acids are present in many processed foods. .
- Omega-5, omega-7 and omega-9 acids are naturally produced by the body, but we also obtain them from the diet.
- Omega-5, omega-7 and omega-9 acids are naturally produced by the body, but we also obtain them from the diet.
- Omega acids affect the health of the cardiovascular, nervous and immune systems, support mental health and have an impact on the appearance and condition of the skin.
- A deficiency of omega acids manifests itself in dry eye and skin deterioration, visual organ disorders, poorer mood, memory and concentration problems.
- An excess of omega acids is rare, and is most often caused by over-supplementation. .
- the heart and circulatory system.
Do you need details?
Omega-3 fatty acids: affect thought processes, concentration, memory, neurotransmission and brain development, reduce blood pressure, reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, neurodegenerative diseases, autoimmune diseases and inflammation.
They are also beneficial for the brain and the body.
They also support skeletal health and muscle regeneration, look after your eyesight and protect against eye disease, reduce the chance of cancer, support sleep, and prevent mental illness. They also support beauty - improving the appearance and condition of your skin and hair.
It is also a valuable component in an athlete's diet, as omega-3 fatty acids benefit performance and renegeration.
Scientific studies have shown the positive effects of polyunsaturated fatty acids in neurodegenerative diseases by, among other things, inhibiting brain cell death..
 .
.
Marcin Zarzycki physician
"According to some researchers, omega-3 fatty acids may have a positive effect on the course of ADHD in children by improving their concentration, but further research is needed on this topic," adds the doctor.
Sources of omega-3
.The most omega-3 fatty acids are found in fatty fish marine fish (7-15% fat content) such as mackerel, sardines, salmon, herring, rainbow trout. Omega-3 fatty acids from fish are better absorbable by the body than plant sources of the valuable acidsand.
In theory, the most omega-3s are found in flaxseed oil. In practice, this is a bit of a misnomer - flaxseed oil is an excellent source of ALA acid, not DHA + EPA, the omega-3s from flaxseed oil are not as well absorbed into the bloodstream as those from fish, and besides, drinking 100g of pure oil is a dubious pleasure...
.There is also the ratio of omega-3 to omega-6, which is hellishly important. Unfortunately, it fares poorly in the case of plant-based products.
The ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 is also important.
Remember: the ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 is crucial for health. I explain what this is all about later in this article.
Remember: the ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 is crucial for health.
The foods richest in omega-3 areand:
.|
Product . |
Content of omega-3 fatty acids in 100 g* |
|
Flaxseed oil |
5300-6000 mg |
|
Chia seeds (chia seeds) . |
5000-6000 mg |
|
Macre³ |
3000-4000 mg |
|
Walnut |
2500-3000 mg |
|
Sardines |
2200-2500 mg |
|
Cod liver oil (tran) |
2400 mg |
|
Salmon |
2100 mg |
|
Herring |
2000-3000 mg |
|
Salmon trout |
1200-1400 mg . |
|
Tuna |
1000-1500 mg |
|
Shrimp |
300-500 mg |
*The content of omega-3 fatty acids in foods can vary depending on a number of factors, e.g. how they are grown or heat treated.
Omega-3 deficiency - symptoms
.The most common cause of omega-3 acid deficiency is a poor diet. In short: not enough fish and related products. You will feel and literally see the deficiency of these valuable fats on your own skin. What should cause you to be concerned?
The most common symptoms of omega-3 fatty acid deficiency are:
.Omega-3 excess - symptoms
.You can overdose on omega-3 fats. An excess of these acids can harm you and lead to 'thinning' of the blood, bleeding in injuries and even an increase in LDL (so-called bad cholesterol) in the bloodand.
Symptoms of excess omega-3 fatty acids:
.There are patients who rely on quantity rather than quality of supplementation. Doing so has little health benefit, and may do harm..
 .
.
Witold Tomaszewskidoctor of medical sciences
.Omega-3 fatty acids in the vege diet
.Vegans and vegetarians are at risk of nutrient deficiencies, such as B vitamins, (especially vitamin B12), iron and omega acids due to the abandonment of fish, meat and egg consumptionand. However, nothing is lost - you can find valuable omega acids in many tasty plant-based products and vegan dietary supplements made from marine algae.
See also:
.Omeega-6 acids
.In a nutshell
The omega-6 acids are LA, GLA and AA, and their proper concentration supports metabolism, protects the heart, nervous system and skin. Soybean, sunflower and corn oils contain the most omega-6. It is important to maintain the correct ratio between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids in the diet - its disruption can lead to inflammation in the body.
Omega-6 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fatty acids that you need to supply to your body with your diet. The most important omega-6 fatty acids areand:
Although in research studiesand some omega-6 fatty acids (e.g. GLA and LA) have been shown to have health-promoting benefits in the management of chronic disease symptoms, these acids are generally the black commodity in the healthy fat family. An excess of AA relative to omega-3 fatty acids may be pro-inflammatory and promote the development of certain diseasesand.
GLA may help reduce the body's signs of inflammation, and CLA may aid fat mass reduction. And lest you leave AA acid with the patch of 'pro-inflammatory' - adequate concentrations of it support the growth and regeneration of the body's cells and positively influence fetal brain development from the 3rd trimester of pregnancy .
This is important
.Omega-6s are found more often and more abundantly in the normal diet so usually do not require supplementation or even monitoring. You are most likely eating too few omega-3s and they are the ones worth focusing on.
Properties of omega-6 acids
.Omega-6 fatty acids take care of:
- blood and brain.
Do you need details?
.Omega-6 fatty acids reduce the risk of heart disease, are essential for brain development and nervous system function already in prenatal life. They are also involved in the processing and storage of fats and in the metabolism of carbohydrates - regulating blood sugar levels, controlling the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream and helping to protect the body against chronic diseases.
They are also involved in the metabolism of fats and in the metabolism of carbohydrates.
Additionally, they are involved in the regulation of inflammation and help maintain the health, appearance and hydration of the skin.
Omeega-3 and 6 acids are used in cosmetics, such as creams. Topical application of oils with these acids improves hydration and skin barrier function. However, the most important thing is to supply these acids with diet in order to enjoy healthy skin..
 .
.
Katarzyna SrebrCosmetologist
Sources of omega-6
.Omega-6 fatty acids are found in many unhealthy processed vegetable oil-based products for example, in fast food or crisps. Omega-6s from healthy sources, on the other hand, are valuable and nutritious.
|
Product . |
Content of omega-6 fatty acids in 100 g* |
|
| . |
Safflower oil |
74,500 mg . |
|
Soybean oil . |
50 960 mg |
|
|
Pumpkin seed oil |
50,000 mg |
|
|
Corn oil |
49,300 mg |
|
|
Sunflower oil |
39 230 mg |
|
|
Almonds |
12,070 mg |
|
|
Chews |
7840 mg |
|
|
Hazelnuts |
7290 mg |
|
|
Walnuts |
7790 mg |
|
|
Pumpkin seeds |
6740 mg |
|
|
Avocado |
3940 mg |
*The content of omega-6 fatty acids in foods can vary depending on a number of factors, e.g. cultivation or heat treatment.
What are the symptoms of omega-6 deficiency?
.The correct ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acids is between 1:1 and 1:4. Such a ratio ensures the correct functioning of all your body systems. An imbalance of these acids will make itself known very quickly.
Obacillary fatty acids are a good source of fatty acids.
Symptoms of omega-6 deficiency or an imbalance between omega-3 and 6 acids and:
An omega-6 deficiency is rare. In addition to the production of these acids by the body, we supply them in abundance with the diet. The symptoms mentioned are not characteristic and may be indicative of other ailments, not necessarily of an imbalance between n-3 and n-6..
 .
.
Witold Tomaszewskidoctor of medical sciences
.Omega-6 excess - symptoms
.Also, too much omega-6 to omega-3 increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and depressionand.
Omega-9 acids
.In a nutshell
.Omega-9 acids are monounsaturated fatty acids that the body produces on its own. These include oleic, nervonic and erucic acids. They support the cardiovascular and nervous systems, mental health and reduce inflammation in the body. Deficiency and excess of omega-9 fatty acids show no clear symptoms. The best sources of omega-9 fatty acids are vegetable oils.
Properties of omega-9 acids
.Omega-9 acids take care of:
- blood and brain.
Do you need details?
.Omega-9s influence heart health and may reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, support brain and nervous system function. They also take part in lowering 'bad' cholesterol (LDL) and increasing 'good' cholesterol (HDL), and may help control blood sugar levels and improve insulin resistance. In addition, omega-9s have been shown to have antidepressant effects, reduce inflammation in the body and support skin healing and regeneration.
Sources of omega-9
.Most omega-9 fatty acids are found in vegetable oils and those produced from seedsand.
.|
Product . |
Content of omega-9 acids in 100 g* |
|
| . |
Rape seed oil |
9220 mg |
|
Olive oil |
7120 mg |
|
|
Avocado oil |
6700 mg |
|
|
Sesame seeds |
6700 mg |
|
|
Pumpkin seeds |
5739 mg |
|
|
Corn oil |
4860 mg |
|
|
Sesame oil |
3900 mg |
|
|
Fat from goose |
3685 mg |
|
|
100% peanut butter |
3440 mg |
|
|
Cashew nuts |
2520 mg |
*The content of omega-9 fatty acids in foods can vary depending on a number of factors, e.g. how they were grown or how they were cooked.
What are the symptoms of omega-9 deficiency?
.A diet deficient in oleic acid (the most important component of omega-9) can lead toand:
Omega-9 excess - symptoms
.Over-supplementation of omega-9 is most often associated with over-supplementation.
Supplementation of omega-9 fatty acids is unnecessary. Our body is able to synthesise them from omega-3 and omega-6 acids..
 .
.
Julia SkrajdaDietitian
.Surprise. The popular trio 3-6-9 are joined by omega-5 and omega-7. What's worth knowing about them?
Omega-5 acids
.Omega-5 (punicic acid) is a polyunsaturated fatty acid. It is made from omega-3 and omega-6and, but is not essential in the body - so it is difficult to speak of a deficiency or excess. A tasty source of it is pomegranate fruit.
What properties does omega-5 acid have?
.It has anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, anti-fungal and anti-bacterial effectsand. It can help lower LDL cholesterol and improve blood vessel function, which in turn contributes to reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease .
Applied to the skin, it can improve its appearance and condition by stimulating the production of collagen and alleviating inflammation .
As much as 70% of all fatty acids in pomegranate seeds are punicic acid. Pomegranates are worth eating for their omega-5, fibre, antioxidants, vitamin E and magnesium..
 .
.
Julia SkrajdaDietitian
.Punicic acid can also be consumed in the form of dietary supplements. If you care about its effect on the skin, you can find creams and lotions with omega-5 in drugstores.
Omega-7 acids
.Omega-7 is a group of acids that the body produces on its ownand. Their exact effects on health require further research. The best known omega-7 acid is palmitoleic acid, which has anti-inflammatory effects, lowers cholesterol, helps control lipid metabolism and alleviates dry eye syndrome.
A deficiency of omega-7 is rare, while an excess can lead to blood clotting disorders and immune system problems. The best sources of omega-7 are sea buckthorn oil, salmon, anchovies, macadamia nuts and avocados.
The best sources of omega-7 are sea buckthorn oil, salmon, anchovies, macadamia nuts and avocados.
Deficiency and excess of omega-7 acids
A deficiency of omega-7s is rareand, but their absence can manifest similarly to a deficiency of other acids - dry skin and eyes. In contrast, an excess of them can result in blood clotting disorders and immune system problems .
The best sources of omega-7 are sea buckthorn oil, wild salmon, anchovies, macadamia nuts and avocados..
 .
.
Julia SkrajdaDietitian
.Important
The first omega-7 supplements are coming on sale.Remember - your body produces this acid on its own, and it is most important for your health to get all the healthy fats evenly through a nutritious and balanced diet.
Daily support of the skin with omega acid supplements has a significant effect on improving hydration and thus delaying the skin ageing process. Many cosmetic manufacturers implement omega 3 fatty acids into their formulations, but in cosmetics they mainly have an occlusive effect by retaining water in the epidermis..
 .
.
Marta Majszyk-Swiatek cosmetologist, cosmetics production technologist, biologist
How many omega acids do you need to consume per day?
.The National Centre for Nutrition Educationand recommends the following dietary intakes of omega acids and fats:
Daily omega acids and fat requirements for adults
. .|
Ingredient . |
Recommended daily allowance . |
|
|
Total fat . |
20-35% of kcal intake . |
|
|
Eicosapentaenoic acid + Docosahexaenoic acid (EHA + DHA) . |
250 mg |
|
|
Linoleic acid (LA) . |
4% of kcal intake from fats | |
|
Alpha-linoleic acid (ALA) . |
0.5% of kcal intake from fats . |
|
|
Saturated fatty acids and trans-fatty acid isomers |
As low as possible | As low as possible. |
It is easy to consume a daily dose of 250 mg EPA + DHA. In practice, this is, for example:
Daily omega acids and fat requirements for infants, children and adolescents
. .|
Ingredient . |
Recommended daily allowance . |
|
|
Total fat . |
> 7-11 months: 40% of kcal from fat 1-3 years: 35-40% from fats 4-18 years: 20-35% of kcal from fats |
|
|
Eicosapentaenoic acid + Docosahexaenoic acid (EHA + DHA) . |
7-24 months: DHA 100 mg/day only; .2-18 years: EPA+DHA 250 mg/day |
|
|
Linoleic acid (LA) . |
4% of kcal intake from fats | |
|
Alpha-linoleic acid (ALA) . |
0.5% of kcal intake from fats . |
|
|
Saturated fatty acids and trans-fatty acid isomers |
As low as possible | As low as possible. |
The recommendations are to eat two portions of fish per week. One portion is approximately 100-150g. Once a week it should be an oily fish (e.g. salmon, mackerel)..
 .
.
Julia SkrajdaDietitian
.Recommended ratio of omega 3 and 6 acids
.The ideal ratio of n-3 to n-6 intake is between 1:1 and 1:4.
.Even at this moment there is an omega-3 vs omega-6 battle going on in your body. You are cheering for omega-3, but you are probably putting more omega-6 on the field...
Good omega, bad omega?
.The most common omega-6 fat is linoleic acid, which the body can convert into, among other things, arachidonic acid (AA). Like EPA (one of the omega-3 fatty acids), AA produces eicosanoids. An excess of eicosanoids can increase the risk of inflammation and disease.
This is why it is so important to have the correct ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 intake.
According to researchers a healthy ratio of n-3 to n-6 fatty acids should be between 1:1 and 1:4. Research suggests that people following the so-called "Western diet" may consume acids in a ratio of... between 1:15 and almost 1:17.
The Western diet is a term for a way of eating that is characterised by a high content of processed foods, fast food, instant products, sugar, salt, red meat, white flour and harmful additives. It is low in vitamins, minerals and fibre..
 .
.
Julia SkrajdaDietitian
."This way of eating leads to the development of many diseases - cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune diseases and even mental disorders," adds the nutritionist.
How to eat omega-3 and omega-6 wisely?
.You may regularly eat wild steamed salmon, but if you otherwise enjoy munching chips for a movie just as often, and supplement your daily coffee with chocolate biscuits, the balance can be upset. Ba, even fresh, natural products like avocados tip the balance towards omega-6.
Do you need to look at tables of omega acid sources when shopping or going out to a restaurant? No. All you need to do is follow a few simple rules:
Most importantly: eat more fish or supplement with omega-3s - simply. There are loads of healthy things to eat regularly. Just looking at the ratio of n-3 to n-6 will paralyse you. Avocados, nuts or olive oil are delicious and healthy, go ahead and have a shake.
Supplementation of omega acids
.Who should supplement omega-3 fatty acids
.How to choose the best products with omega acids?
.Pay attention to the source of the acids.
.Choose omega-3 supplements from wild fish. Fish living in the wild eat algae and produce their own omega acids. Most farmed fish contain less omega acids because they are fed "artificially"..
 .
.
Ilona Krzak Master of Pharmacy
Take the right daily dose to suit your needs.
.The average adult should consume 250 mg of EPA + DHA daily.
Note
It makes no sense to consume larger amounts "to stock up" - the body gets rid of excess omega acids.
Choose the best form of dietary supplement.
.Scientific studies have shownand that omega-3 oils in emulsified forms absorb better than in pure form (e.g. from ordinary oil). "Emulsified" oil is oil that has been mixed with water and an emulsifier, so that it forms a stable emulsion.
Such a liquid can be consumed in capsules or from a bottle.
- .
Omega acids for children
.The best form of omega-3 for children is liquid or drops. This is a more convenient dosage form and more convenient to administer than capsules. Try to choose a product without sugar, glucose-fructose syrup, sweeteners or synthetic flavours.
I am not in favour of omega-3 forms for children such as coloured jelly beans. They contain more sugar than the omega acids themselves..
 .
.
Ilona Krzak Master of Pharmacy
See also:
.Why omega 3-6-9 supplements are a waste of money and... health?
.While I was preparing to write this article, my browser was fat-burnt - advertisements for dietary supplements with omega acids were popping up everywhere. My attention was particularly drawn to the so-called "3-6-9" preparations, i.e. containing as many as three acids in one capsule.
I asked the experts for their opinion on this.
.Supplementation with omega 3-6-9 products is not justified. The omega-9 acids are produced by our body, and by taking omega-3 and omega-6 in addition, we may unknowingly create a large imbalance between them, which will adversely affect health.
.. .
Witold Tomaszewskidoctor of medical sciences
.
The omega acids compete with each other for 'priority' of absorption and if we consume more omega-6,-7 and -9 than omega-3, their ratio will be distorted in favour of the former. Omega-3s may not be absorbed or only absorbed in small amounts..
 .
.
Julia SkrajdaDietitian
.The conclusion follows - omega 3-6-9 fatty acids are best obtained from a varied and nutritious diet.
Is an overdose of omega acids possible?
.Luckily, you don't have to worry about overdosing on omega acids from your diet. A clinical nutritionist explains:
It is difficult to overdose on omega acids from food. The body has mechanisms that deal with excretion of the excess. It is dangerous to over-supplement omega 6 and 9 while not supplementing omega-3, or to supplement omega 3-6-9 because of the mutual exclusion of the acids, leading to a deficiency of one and an excess of the other..
 .
.
Julia SkrajdaDietitian
.Can you test for omega acid deficiency?
.Yes, testing for omega-3 fatty acids involves assessing the serum levels of EPA and DHA.
The result indicates to what extent the patient's cardiovascular system is protected. It also serves the early prevention of diet-related diseases. The average price of the test is around £200.
.Omega acids in the diet of Poles
.Unfortunately, Poles eat very little fish. When we argue what to have for dinner (schabowy or mince?), such Norwegians simply eat their favourite fish.
This is not an exaggeration -
.According to the FAO (Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations)and the biggest consumers of fish in the world are Norwegians. The average Norwegian eats about 46 kg of fish per year. A Pole - only 14 kg. This means that Norwegians eat twice as much omega-3 per day as Poles (about 1.7 g vs 0.9 g).
How to include omega acids in your diet?
.I know that fish, nuts and seeds are expensive, but I have some useful tips for you on how to buy products rich in omega-3 fatty acids sensibly.
See also: Best sources of omega-3 in the diet
Contraindications to omega acid supplementation
.Interactions - what not to combine omega acids with?
.Dietary supplements with omega acids may interact with medications that affect blood clotting, such as aspirin, warfarin or heparinand. Consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting supplements so that you do not harm yourself.
See also:
.Summary
.FAQ
.What are the best omega acids?
.Recommended omega acids is the dietary supplement Natu.Care Premium Omega-3 TG 750 mg. It contains the optimum ratio of omega-3 fatty acids (2:1), namely 250 mg of DHA and 500 mg of EPA, in the highly bioavailable form of triglycerides.
What are the best omega acids for joints?
.Green unsaturated fatty acids omega-3 and omega-6 are responsible for regulating inflammatory processes in the body and are therefore important in preventing the development of musculoskeletal diseases and supporting the treatment of diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Consuming the correct proportion of them in the diet enables the body to function properly and control inflammation. Supplementation with omega-3 tablets
may be beneficial.How much omega acids to consume during pregnancy and lactation?
.Pregnant and breastfeeding women should consume DHA and EPA acids at 250 mg/day and an additional 100-200 mg DHA/day. The Polish Gynaecological Society recommends up to 600 mg of DHA daily and as much as 1,000 mg in women at risk of preterm birth. Almost 90% of pregnant Polish women consume less than the recommended 200 mg of DHA for health.
Which omega acids are the healthiest?
.The healthiest, most popular and well-researched are omega-3 acids. They have been shown in scientific studies to have a range of health-promoting benefits: from fetal life they support the function of many body systems, may protect against the development of cancer, support mental health and the appearance of skin and hair. Deficiencies of omega-3 fatty acids are common, so it is worth sourcing them from the diet or good quality supplements (omega-3 tablets).
How long can omega-3 acids be used?
.Dietary supplements with omega-3 fatty acids can be used all year round if the diet is poor in foods rich in healthy fats. Year-round supplementation (e.g. tranium) should be consulted with your doctor or advised by a dietitian on how to naturally incorporate foods with these healthy fats into your diet.
Scientific research suggests that the minimum period of omega acid supplementation to see improvements in microbiota and body health is 6 months.
Is there vitamin D in omega-3 fatty acids?
.No, there is no vitamin D in omega-3 acids as a chemical compound. The combination of omega acids and vitamin D3 can be found in dietary supplements. Taking preparations with omega acids and vitamin D3 in drops positively influences the organism and supplements common in Poland deficiencies of these two components.
Vitamin D deficiency is as dangerous as omega-3 fatty acids.
Do omega acids lower cholesterol?
.No, omega-3 acids do not lower bad LDL cholesterol. In fact, an excess of omega-3 fatty acids may even increase it, which adversely affects the lipidogram (body fat management). The overall ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 acids is important for the proper functioning of the cardiovascular system.
What omega-3 fatty acids to choose?
.The best omega-3 acids come from wild-caught fish, which naturally eat the algae and produce their own acids. According to scientific research, the emulsified form of omega-3 oil retains the most health benefits, which can be found in capsules, drops or liquids, preferably in dark packaging. This protects the emulsion from the harmful effects of sunlight.
Sources
.See all
.Abdullah, M., Jowett, B., Whittaker, P. J., & Patterson, L. (2019). The effectiveness of omega-3 supplementation in reducing ADHD associated symptoms in children as measured by the Conners' rating scales: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 110, 64-73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2018.12.002
Agostoni, C., Trojan, S., Bellù, R., Riva, E., Bruzzese, M. G., & Giovannini, M. (1997). Developmental quotient at 24 months and fatty acid composition of diet in early infancy: A follow up study. Archives of Disease in Childhood, 76(5), 421-424. https://doi.org/10.1136/adc.76.5.421
Amjad Khan, W., Chun-Mei, H., Khan, N., Iqbal, A., Lyu, S.-W., & Shah, F. (2017). Bioengineered Plants Can Be a Useful Source of Omega-3 Fatty Acids. BioMed Research International, 2017, 7348919. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7348919
Balanzá-Martínez, V., Fries, G. R., Colpo, G. D., Silveira, P. P., Portella, A. K., Tabarés-Seisdedos, R., & Kapczinski, F. (2011). Therapeutic use of omega-3 fatty acids in bipolar disorder. Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics, 11(7), 1029-1047. https://doi.org/10.1586/ern.11.42
Balbás, G. M., Regaña, M. S., & Millet, P. U. (2011). Study on the use of omega-3 fatty acids as a therapeutic supplement in treatment of psoriasis. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology, 4, 73-77. https://doi.org/10.2147/CCID.S17220
Balić, A., Vlašić, D., Žužul, K., Marinović, B., & Bukvić Mokos, Z. (2020). Omega-3 Versus Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in the Prevention and Treatment of Inflammatory Skin Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(3), Article 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030741
Biomarkers of Dietary Omega-6 Fatty Acids and Incident Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality | Circulation. (n.d.). Retrieved March 23, 2023, from https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.038908
Blanchard, L. B., & McCarter, G. C.. (2015). Insomnia and exacerbation of anxiety associated with high-EPA fish oil supplements after successful treatment of depression. Oxford Medical Case Reports, 2015(3), 244-245. https://doi.org/10.1093/omcr/omv024
Bolhuis, D. P., Newman, L. P., & Keast, R. S. J. (2016). Effects of Salt and Fat Combinations on Taste Preference and Perception. Chemical Senses, 41(3), 189-195. https://doi.org/10.1093/chemse/bjv079
Bradberry, J. C., & Hilleman, D. E. (2013). Overview of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Therapies. Pharmacy and Therapeutics, 38(11), 681-691.
Calder, P. C. (2010). Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Inflammatory Processes. Nutrients, 2(3), 355-374. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu2030355
Calder, P. C. (2015). Functional Roles of Fatty Acids and Their Effects on Human Health. JPEN. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition, 39(1 Suppl), 18S-32S. https://doi.org/10.1177/0148607115595980
Canhada, S., Castro, K., Perry, I. S., & Luft, V. C. (2018). Omega-3 fatty acids' supplementation in Alzheimer's disease: A systematic review. Nutritional Neuroscience, 21(8), 529-538. https://doi.org/10.1080/1028415X.2017.1321813
Chauhan, S., Kodali, H., Noor, J., Ramteke, K., & Gawai, V. (2017). Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Lipid Profile in Diabetic Dyslipidaemia: a Single Blind, Randomised Clinical Trial. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research : JCDR, 11(3), OC13-OC16. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2017/20628.9449
Chávaro-Ortiz, L. I., Tapia, B. D., Rico-Hidalgo, M., Gutiérrez-Aguilar, R., & Frigolet, M. E. (2022). Trans-palmitoleic acid reduces adiposity via increased lipolysis in a rodent model of diet-induced obesity. The British Journal of Nutrition, 127(6), 801-809. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114521001501
Conquer, J. A., & Holub, B. J. (1996). Supplementation with an algae source of docosahexaenoic acid increases (n-3) fatty acid status and alters selected risk factors for heart disease in vegetarian subjects. The Journal of Nutrition, 126(12), 3032-3039. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/126.12.3032
Cordova-Gallardo, J. (2021). Effect of Omega-5 Fatty Acid Supplement on Markers of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Patients With Severe Alcoholic Hepatitis Treated With ... (Clinical trial registration No. NCT03732586). clinicaltrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03732586
Derbyshire, E. (2017). Do Omega-3/6 Fatty Acids Have a Therapeutic Role in Children and Young People with ADHD? Journal of Lipids, 2017, 6285218. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6285218
DiNicolantonio, J. J., & O'Keefe, J. H. (2018). Importance of maintaining a low omega-6/omega-3 ratio for reducing inflammation. Open Heart, 5(2), e000946. https://doi.org/10.1136/openhrt-2018-000946
Djuricic, I., & Calder, P. C. (2021). Beneficial Outcomes of Omega-6 and Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Human Health: An Update for 2021. Nutrients, 13(7), 2421. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072421
Dry Eye Assessment and Management Study Research Group, Asbell, P. A., Maguire, M. G., Pistilli, M., Ying, G., Szczotka-Flynn, L. B., Hardten, D. R., Lin, M. C., & Shtein, R. M. (2018). N-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation for the Treatment of Dry Eye Disease. The New England Journal of Medicine, 378(18), 1681-1690. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1709691
Dyall, S. C. (2015). Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids and the brain: A review of the independent and shared effects of EPA, DPA and DHA. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 7, 52. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2015.00052
Effects of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on platelet function in healthy subjects and subjects with cardiovascular disease-PubMed. (n.d.). Retrieved 22 March 2023, from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23329646/
Erratum for Konstantinidou et al. Personalized nutrition and cardiovascular disease prevention: From Framingham to PREDIMED. Adv Nutr 2014;5:368S-71S. (2015). Advances in Nutrition, 6(5), 627. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.115.009266
Finucane, O. M., Lyons, C. L., Murphy, A. M., Reynolds, C. M., Klinger, R., Healy, N. P., Cooke, A. A., Coll, R. C., McAllan, L., Nilaweera, K. N., O'Reilly, M. E., Tierney, A. C., Morine, M. J., Alcala-Diaz, J. F., Lopez-Miranda, J., O'Connor, D. P., O'Neill, L. A., McGillicuddy, F. C., & Roche, H. M. (2015). Monounsaturated Fatty Acid-Enriched High-Fat Diets Impede Adipose NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated IL-1β Secretion and Insulin Resistance Despite Obesity. Diabetes, 64(6), 2116-2128. https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-1098
FoodData Central. (n.d.). Retrieved March 23, 2023, from https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/
Friday, K. E., Childs, M. T., Tsunehara, C. H., Fujimoto, W. Y., Bierman, E. L., & Ensinck, J. W. (1989). Elevated plasma glucose and lowered triglyceride levels from omega-3 fatty acid supplementation in type II diabetes. Diabetes Care, 12(4), 276-281. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.12.4.276
Frigolet, M. E., & Gutiérrez-Aguilar, R. (2017). The Role of the Novel Lipokine Palmitoleic Acid in Health and Disease123. Advances in Nutrition, 8(1), 173S-181S. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.115.011130
Fritsche, K. L. (2015). The Science of Fatty Acids and Inflammation123. Advances in Nutrition, 6(3), 293S-301S. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.114.006940
Garg, A. (1998). High-monounsaturated-fat diets for patients with diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 67(3), 577S-582S. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/67.3.577S
Gerster, H. (1998). Can adults adequately convert alpha-linolenic acid (18:3n-3) to eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5n-3) and docosahexaenoic acid (22:6n-3)? International Journal for Vitamin and Nutrition Research. Internationale Zeitschrift Fur Vitamin- Und Ernahrungsforschung. Journal International De Vitaminologie Et De Nutrition, 68(3), 159-173.
Grosso, G., Galvano, F., Marventano, S., Malaguarnera, M., Bucolo, C., Drago, F., & Caraci, F. (2014). Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Depression: Scientific Evidence and Biological Mechanisms. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2014, 313570. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/313570
Guerra-Vázquez, C. M., Martínez-Ávila, M., Guajardo-Flores, D., & Antunes-Ricardo, M. (2022). Punicic Acid and Its Role in the Prevention of Neurological Disorders: A Review. Foods, 11(3), Article 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11030252
Helland, I. B., Smith, L., Saarem, K., Saugstad, O. D., & Drevon, C. A. (2003). Maternal supplementation with very-long-chain n-3 fatty acids during pregnancy and lactation augments children's IQ at 4 years of age. Pediatrics, 111(1), e39-44. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.111.1.e39
Hunt CE, Engel RR, Modler S, Hamilton W, Bissen S, Holman RT. Essential fatty acid deficiency in neonates: inability to reverse deficiency by topical applications of EFA-rich oil. J Pediatr. 1978;92(4):603-607.
Innis, S. M. (2008). Dietary omega 3 fatty acids and the developing brain. Brain Research, 1237, 35-43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2008.08.078
Jarosz, M., & Taraszewska, A. (2014). Risk factors for gastroesophageal reflux disease: The role of diet. Przegla̜d Gastroenterological, 9(5), 297-301. https://doi.org/10.5114/pg.2014.46166
Jarosz, Prof Dr n med M. (2020, December 3). Nutrition Standards 2020. National Center for Nutrition Education. https://ncez.pzh.gov.pl/abc-zywienia/normy-zywienia-2020/
Kawamura, A., Ooyama, K., Kojima, K., Kachi, H., Abe, T., Amano, K., & Aoyama, T. (2011). Dietary supplementation of gamma-linolenic acid improves skin parameters in subjects with dry skin and mild atopic dermatitis. Journal of Oleo Science, 60(12), 597-607. https://doi.org/10.5650/jos.60.597
Khodarahmi, M., & Azadbakht, L. (2016). Dietary fat intake and functional dyspepsia. Advanced Biomedical Research, 5, 76. https://doi.org/10.4103/2277-9175.180988
Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K., Belury, M. A., Andridge, R., Malarkey, W. B., & Glaser, R. (2011). Omega-3 supplementation lowers inflammation and anxiety in medical students: A randomized controlled trial. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 25(8), 1725-1734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2011.07.229
Krupa, K., Fritz, K., & Parmar, M. (2023). Omega-3 Fatty Acids. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564314/
Le Floc'h, C., Cheniti, A., Connétable, S., Piccardi, N., Vincenzi, C., & Tosti, A. (2015). Effect of a nutritional supplement on hair loss in women. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 14(1), 76-82. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.12127
Leaf, A. (2008). Historical overview of n-3 fatty acids and coronary heart disease. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 87(6), 1978S-80S. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/87.6.1978S
Löfvenborg, J. E., Andersson, T., Carlsson, P.-O., Dorkhan, M., Groop, L., Martinell, M., Tuomi, T., Wolk, A., & Carlsson, S. (2014). Fatty fish consumption and risk of latent autoimmune diabetes in adults. Nutrition & Diabetes, 4(10), e139. https://doi.org/10.1038/nutd.2014.36
Lyu, X., Agar, O. T., Barrow, C. J., Dunshea, F. R., & Suleria, H. A. R. (2023). Phenolic Compounds Profiling and Their Antioxidant Capacity in the Peel, Pulp, and Seed of Australian Grown Avocado. Antioxidants, 12(1), Article 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12010185
Marine Oils. (2006). In Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK501898/
Martins, J. G. (2009). EPA but not DHA appears to be responsible for the efficacy of omega-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation in depression: Evidence from a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 28(5), 525-542. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2009.10719785
Merle, B. M. J., Benlian, P., Puche, N., Bassols, A., Delcourt, C., Souied, E. H., & Nutritional AMD Treatment 2 Study Group. (2014). Circulating omega-3 Fatty acids and neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 55(3), 2010-2019. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.14-13916
Mischoulon, D., & Freeman, M. P. (2013). Omega-3 fatty acids in psychiatry. The Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 36(1), 15-23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psc.2012.12.002
Naini, A. E., Keyvandarian, N., Mortazavi, M., Taheri, S., & Hosseini, S. M. (2015). Effect of Omega-3 fatty acids on blood pressure and serum lipids in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients. Journal of Research in Pharmacy Practice, 4(3), 135-141. https://doi.org/10.4103/2279-042X.162356
Office of Dietary Supplements-Omega-3 Fatty Acids. (n.d.). Retrieved March 16, 2023, from https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Omega3FattyAcids-Consumer/
Omega-9 Fatty Acid-An overview | ScienceDirect Topics. (n.d.). Retrieved March 23, 2023, from https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/omega-9-fatty-acid
Palmitoleic Acid-An overview | ScienceDirect Topics. (n.d.). Retrieved March 23, 2023, from https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/palmitoleic-acid
Patterson, E., Wall, R., Fitzgerald, G. F., Ross, R. P., & Stanton, C. (2012). Health Implications of High Dietary Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, 2012, 539426. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/539426
Pecora, F., Persico, F., Argentiero, A., Neglia, C., & Esposito, S. (2020). The Role of Micronutrients in Support of the Immune Response against Viral Infections. Nutrients, 12(10), 3198. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103198
Pei-Chen Chang, J. (2021). Personalised medicine in child and Adolescent Psychiatry: Focus on omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and ADHD. Brain, Behavior, & Immunity - Health, 16, 100310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbih.2021.100310
Pieniak, Z., Kołodziejczyk, M., Kowrygo, B., & Verbeke, W. (2011). Consumption patterns and labelling of fish and fishery products in Poland after the EU accession. Food Control, 843-850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2010.09.022
Rossmeisl, M., Pavlisova, J., Bardova, K., Kalendova, V., Buresova, J., Kuda, O., Kroupova, P., Stankova, B., Tvrzicka, E., Fiserova, E., Horakova, O., & Kopecky, J. (2020). Increased plasma levels of palmitoleic acid may contribute to beneficial effects of Krill oil on glucose homeostasis in dietary obese mice. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids, 1865(8), 158732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2020.158732
Saunders, A. V., Davis, B. C., & Garg, M. L. (2013). Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and vegetarian diets. The Medical Journal of Australia, 199(S4), S22-26. https://doi.org/10.5694/mja11.11507
Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and maintenance of normal (fasting) blood concentrations of triglycerides (ID 533, 691, 3150), protection of blood lipids from oxidative damage (ID 630), contribution to the maintenance or achievement of a normal body weight (ID 629), brain, eye and nerve development (ID 627, 689, 704, 742, 3148, 3151), maintenance of normal brain function (ID 565, 626, 631, 689, 690, 704, 742, 3148, 3151), maintenance of normal vision (ID 627, 632, 743, 3149) and maintenance of normal spermatozoa motility (ID 628) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006 | EFSA. (2010, October 19). https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/1734
Shabbir, M. A., Khan, M. R., Saeed, M., Pasha, I., Khalil, A. A., & Siraj, N. (2017). Punic acid: A striking health substance to combat metabolic syndromes in humans. Lipids in Health and Disease, 16, 99. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-017-0489-3
Simopoulos, A. P. (2002). The importance of the ratio of omega-6/omega-3 essential fatty acids. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 56(8), 365-379. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0753-3322(02)00253-6
Simopoulos, A. P. (2008). The Importance of the Omega-6/Omega-3 Fatty Acid Ratio in Cardiovascular Disease and Other Chronic Diseases. Experimental Biology and Medicine, 233(6), 674-688. https://doi.org/10.3181/0711-MR-311
Simopoulos, A. P. (2016). An Increase in the Omega-6/Omega-3 Fatty Acid Ratio Increases the Risk for Obesity. Nutrients, 8(3), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8030128
Simopoulos, A. P., & DiNicolantonio, J. J. (2016). The importance of a balanced ω-6 to ω-3 ratio in the prevention and management of obesity. Open Heart, 3(2), e000385. https://doi.org/10.1136/openhrt-2015-000385
Siscovick, D. S., Barringer, T. A., Fretts, A. M., Wu, J. H. Y., Lichtenstein, A. H., Costello, R. B., Kris-Etherton, P. M., Jacobson, T. A., Engler, M. B., Alger, H. M., Appel, L. J., Mozaffarian, D., & American Heart Association Nutrition Committee of the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health; Council on Epidemiology and Prevention; Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young; Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing; and Council on Clinical Cardiology. (2017). Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid (Fish Oil) Supplementation and the Prevention of Clinical Cardiovascular Disease: A Science Advisory From the American Heart Association. Circulation, 135(15), e867–e884. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000482
Song, I.-B., Gu, H., Han, H.-J., Lee, N.-Y., Cha, J.-Y., Son, Y.-K., & Kwon, J. (2018). Omega-7 inhibits inflammation and promotes collagen synthesis through SIRT1 activation. Applied Biological Chemistry, 61(4), Article 4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13765-018-0377-1
Souza, C. O., Teixeira, A. A. S., Lima, E. A., Batatinha, H. A. P., Gomes, L. M., Carvalho-Silva, M., Mota, I. T., Streck, E. L., Hirabara, S. M., & Rosa Neto, J. C. (2014). Palmitoleic acid (n-7) attenuates the immunometabolic disturbances caused by a high-fat diet independently of PPARα. Mediators of Inflammation, 2014, 582197. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/582197
Stark, A. H., Crawford, M. A., & Reifen, R. (2008). Update on alpha-linolenic acid. Nutrition Reviews, 66(6), 326-332. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-4887.2008.00040.x
Sublette, M. E., Ellis, S. P., Geant, A. L., & Mann, J. J. (2011). Meta-analysis of the effects of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) in clinical trials in depression. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 72(12), 1577-1584. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.10m06634
Tanghetti, E. A. (2013). The Role of Inflammation in the Pathology of Acne. The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, 6(9), 27-35.
The State of World Fisheries 2022 | FAO | Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. (n.d.). https://doi.org/10.4060/cc0461en
Vermel', A. E. (2005). [Clinical application of omega-3-fatty acids (cod-liver oil)]. Klinicheskaia Meditsina, 83(10), 51-57.
.Wang, C., Harris, W. S., Chung, M., Lichtenstein, A. H., Balk, E. M., Kupelnick, B., Jordan, H. S., & Lau, J. (2006). n-3 Fatty acids from fish or fish-oil supplements, but not alpha-linolenic acid, benefit cardiovascular disease outcomes in primary- and secondary-prevention studies: A systematic review. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 84(1), 5-17. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/84.1.5
Wielgosz, Ph.D., R.W., Prof NIZP PZH-PIB, M.Sc. Justyna. (2020, July 27). Importance of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) during pregnancy and lactation. National Center for Nutrition Education. https://ncez.pzh.gov.pl/ciaza-i-macierzynstwo/znaczenie-kwasu-dokozaheksaenowego-dha-w-okresie-ciazy-i-laktacji/
Wawryszuk, N. (2023). Omega acids. Everything you need to know (B. Turczynski, Ed.; 1st ed.). Natu.Care. https://books.google.com/books?vid=9788396887818
.Editorials
Meet the team


Editor
Graduate of Journalism and Artes Liberales at the University of Warsaw. Since 2017, he has been working with the biggest portals in Poland and abroad as an editor. Previously worked for 3 years in one of the leading pharmaceutical companies - he knows the health and beauty industry inside out. In his free time, he most enjoys playing tennis or skiing.

Omega-3 fatty acids are a useful dietary supplement for active people - improves performance and fitness.

Omega-3 in a good dose and an optimum ratio of DHA and EPA acids will replenish valuable fats in the diet.

The omega-3 acids from Natu.Care are distinguished by their triglyceride form, which is characterised by high bioavailability.


