Vitamin B2 - what it is, properties, deficiency, dosage
Vitamin B2 is responsible for cell growth, fat breakdown and energy production.


Learn more about our editorial process
.

Learn more about our editorial process
.

Learn more about our editorial process
.

Learn more about our editorial process
.
Why you can trust us
Articles on Natu.Care are written based on scientific research, data from government websites and other reliable sources. The texts are written in cooperation with doctors, nutritionists and other health and beauty experts. Articles are reviewed before publication and during significant updates.
.Learn more about our editorial process
.Information about advertisements
Content on Natu.Care may contain links to products from the sale of which we may receive a commission. When creating content, we adhere to high editorial standards and take care to be objective about the products discussed. The presence of affiliate links is not dictated by our partners, and we select the products we review ourselves completely independently.
.Learn more about our terms and Conditions
.Vitamin B2 (a.k.a. riboflavin) plays a key role in fat and protein metabolism. It is important for liver, hair, eye and skin health. Find out the most important information about vitamin B2 below.
Tuna, salmon or chicken breast? I choose tuna, but all of these foods will provide you with a solid dose of vitamin B2. Together with a master pharmacist and clinical nutritionist, I have put together a collection of the most important information about vitamin B2. Properties, sources, requirement, deficiency and excess of vitamin B2. All this, you will find in this article. I invite you to read it!
In this article you will find out:
.- What is vitamin B2 .
- What are the sources and key properties of vitamin B2 .
- How to dose this vitamin correctly .
- What are the risk factors, as well as the symptoms and effects of B2 deficiency or excess .

Odkryj, co dla Twojej urody może zrobić Natu.Care Glow Stories
Skóra, włosy, paznokcie: Glow Stories
Wesprzyj prawidłowy stan skóry, włosów i paznokci i ochroń komórki przed stresem oksydacyjnym!
Sprawdź cenę
Glow Stories to formuła aktywnych składników, które zostały starannie dobrane wedle najnowszych badań naukowych. Znajdziesz w nich biotynę, cynk i miedź pielęgnujące zdrowie włosów i promiennej cery. Ponadto cynk jest odpowiedzialny także za zachowanie zdrowych paznokci. Mądra suplementacja zadba o Twoje piękno od środka.Julia Skrajda, dietetyk kliniczny
See also:
- B vitamins [properties + where they occur] .
- Vitamin B1 (thiamine) [properties + where it occurs] .
- Vitamin B3 [properties + where it occurs] .
- Niacin [what it is + effects and side effects] .
- Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) [what it is + properties and excess] .
- Vitamin B6 [where it occurs + deficiency, excess and properties]
- Biotin [what it is + properties and side effects] .
- Biotin for hair [what it gives and effects + ranking]
- Vitamin B9 (folic acid) [what it is + properties and excess] .
- Vitamin B12 [what it helps with + where it occurs] .
- Magnesium [what it is in + properties] .
- Best magnesium [ranking + pharmacist's opinion] .
What is vitamin B2?
.
Vitamin B2 is a solubleand in water B vitamin. It is also known as riboflavin, and its impact on the health of our bodies is significant. Vitamin B2 affects skin health, digestive function and also brain function. Most of it is found in red meat, fish and grains.
Vitamin B2 is added to foods as a colouring agent to give products a yellow colour - E101..
 .
.
Julia SkrajdaDietitian
.Are you interested in the topic of B vitamins?
.Vitamin B2 - properties
.
Vitamin B2 influences numerous processes in our body. We are incapable of producing it, so we need to supply it with our diet. Find out why it is important to ensure adequate levels of vitamin B2 in the body.
How does vitamin B2 work?
.
Prevents headaches
.
Vitamin B2 counteracts headaches as well as migraines. Doctors have long prescribed it to people who struggle with such problemsand. Vitamin B2 supplementation combats headaches and also reduces the frequency of migraines. What's more, it can even shorten their durationand.
Promotes the treatment of anaemia
.
Insufficient concentrations of iron, vitamin B12, folic acid or copper in the body lead to anaemia (anaemia). Studiesand suggest that vitamin B2 can both treat and prevent anaemia.
It doesn't stop there, this vitamin is also responsible for maintaining normal levels of homocysteine (an amino acid that is formed during the formation of proteins) in the bloodand.
Promotes eye health
.
Preliminary research suggests that vitamin B2 deficiency can lead to eye problems such as glaucoma. This is a dangerous eye disease that, in the long term, can even result in blindness. Despite this, the role of vitamin B2 in supporting eye health requires further research.
Fights free radicals
.
Vitamin B2 has antioxidant properties, meaning it fights free radicalsand. This has the effect of delaying the ageing process, as well as preventing conditions such as Alzheimer's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Furthermore, vitamin B2 maintains a state of homeostasis (balance) in our body.
Vitamin B2 is responsible for DNA repair, fatty acid and amino acid synthesis and folic acid. It is also involved in the metabolism of fats, proteins and carbohydrates. Vitamin B2 mediates energy production. It activates and produces glutathione, hence its strong antioxidant properties..
 .
.
Julia SkrajdaDietitian
.Positive for hair and skin
.
Vitamin B2 is responsible for the concentration of collagen in the bodyand. The result is its impact on skin and hair health. Vitamin B2 deficiency, like collagen deficiency, will result in the appearance of wrinkles, as well as the deterioration of hair.
How else does vitamin B2 work?
.
- .
- Promotesand the function of the liver.
- Play an important role in the metabolism of fats, proteins and carbohydratesand. .
- Influences the production of red blood cells (responsible for transporting oxygen in the body ).
- Responsible for the growth and development of cells in the body . .
The absorption of riboflavin, which is stored in the liver, takes place in the small intestine. Its excretion, on the other hand, is related to the function of thyroid hormones. These have the effect of increasing the conversion of vitamin B2 into coenzymes. These are small molecules responsible for the construction of enzymes. Without coenzymes, the work of metabolism is impossible..
 .
.
Julia SkrajdaDietitian
..
Dr Jacob's Melatonin + B12

- Active ingredients: melatonin, vitamin B12
- Form: sucking pastilles .
- Dosage: 1 lozenge per day .
- Sufficient for: 60 days .
Product description
Sweet pleasures in the evening are rather forbidden. Well, unless it's cherry lozenges with melatonin and vitamin B12, whichóre going to improve the quality of your sleep.
One tablet in the evening will shorten your sleep time and stop you waking up.
One tablet in the evening will shortenóyour time to fall asleep and stop you waking up during the night. The addition of vitamin B12 will improve the functioning of the nervous system, making you even better rested.
The following tablets will help to improve the quality of your sleep.
Pros and cons
Sweet pleasures in the evening are rather forbidden. Well, unless it's cherry lozenges with melatonin and vitamin B12, whichóre going to improve the quality of your sleep.
One tablet in the evening will shorten your sleep time and stop you waking up.
One tablet in the evening will shortenóyour time to fall asleep and stop you waking up during the night. The addition of vitamin B12 will improve the functioning of the nervous system, making you even better rested.
The following tablets will help to improve the quality of your sleep.
Additional information
Sweet pleasures in the evening are rather forbidden. Well, unless it's cherry lozenges with melatonin and vitamin B12, whichóre going to improve the quality of your sleep.
One tablet in the evening will shorten your sleep time and stop you waking up.
One tablet in the evening will shortenóyour time to fall asleep and stop you waking up during the night. The addition of vitamin B12 will improve the functioning of the nervous system, making you even better rested.
The following tablets will help to improve the quality of your sleep.
User review
Sweet pleasures in the evening are rather forbidden. Well, unless it's cherry lozenges with melatonin and vitamin B12, whichóre going to improve the quality of your sleep.
One tablet in the evening will shorten your sleep time and stop you waking up.
One tablet in the evening will shortenóyour time to fall asleep and stop you waking up during the night. The addition of vitamin B12 will improve the functioning of the nervous system, making you even better rested.
The following tablets will help to improve the quality of your sleep.
SOLGAR natural vitamin B12

- Active ingredients: vitamin B12
- Form: tablets .
- Packaging: 100 tablets .
- Dose: 1 tablet daily .
- Sufficient for: 100 days .
Product description
The dietary supplement is a source of valuable vitamin B12 in a form that is easily absorbed by humans - cyanocobalamin. This biologically active form of vitamin B12 has many very important protective functions for the body.
Vitamin B12 supports the functioning of the immune system. It also contributes to reducing feelings of fatigue and tiredness. Its important function is also to take part in the metabolism of homocysteine, an amino acid thatós naturally formed in the human body.
Vitamin B12 is a very important protective function.
Pros and cons
The dietary supplement is a source of valuable vitamin B12 in a form that is easily absorbed by humans - cyanocobalamin. This biologically active form of vitamin B12 has many very important protective functions for the body.
Vitamin B12 supports the functioning of the immune system. It also contributes to reducing feelings of fatigue and tiredness. Its important function is also to take part in the metabolism of homocysteine, an amino acid thatós naturally formed in the human body.
Vitamin B12 is a very important protective function.
Additional information
The dietary supplement is a source of valuable vitamin B12 in a form that is easily absorbed by humans - cyanocobalamin. This biologically active form of vitamin B12 has many very important protective functions for the body.
Vitamin B12 supports the functioning of the immune system. It also contributes to reducing feelings of fatigue and tiredness. Its important function is also to take part in the metabolism of homocysteine, an amino acid thatós naturally formed in the human body.
Vitamin B12 is a very important protective function.
User review
The dietary supplement is a source of valuable vitamin B12 in a form that is easily absorbed by humans - cyanocobalamin. This biologically active form of vitamin B12 has many very important protective functions for the body.
Vitamin B12 supports the functioning of the immune system. It also contributes to reducing feelings of fatigue and tiredness. Its important function is also to take part in the metabolism of homocysteine, an amino acid thatós naturally formed in the human body.
Vitamin B12 is a very important protective function.
Aura Herbals Vitamin B Complex drops
Product description
Vegan drops with a complex of B vitamins. A daily serving covers 100% of the requirement for these vitamins. B vitamins are important for the proper functioning of the body, especially for the nervous system, metabolism and energy production.
Pros and cons
Vegan drops with a complex of B vitamins. A daily serving covers 100% of the requirement for these vitamins. B vitamins are important for the proper functioning of the body, especially for the nervous system, metabolism and energy production.
Additional information
Vegan drops with a complex of B vitamins. A daily serving covers 100% of the requirement for these vitamins. B vitamins are important for the proper functioning of the body, especially for the nervous system, metabolism and energy production.
Vitamin B2 - dosage
.
Dosage of vitamin B2 depends on your age. Check the table below and find out how much vitamin B2 you and your loved ones need.
|
Age . |
Recommended daily allowance of vitamin B2*and |
|
0-6 months |
0.3 mg |
|
7-11 months |
0.4 mg |
|
1-3 years |
0.5 mg |
|
4-6 years |
0.6 mg |
|
7-9 years |
0.9 mg |
|
10-12 years |
1 mg |
|
13+ years old female |
1.1 mg |
|
13+ years old men |
1.3 mg |
*Norms for the Polish population
.
Are you pregnant? Or are you breastfeeding? If so, you should provide your body with more vitamin B2. Women who are expecting a baby need to take 1.4 mg of vitamin B2 per day. Ladies who are breastfeeding, on the other hand, need even more - 1.6 mg. Where to get the beneficial vitamin B2 from?
.
Vitamin B2 - sources
.
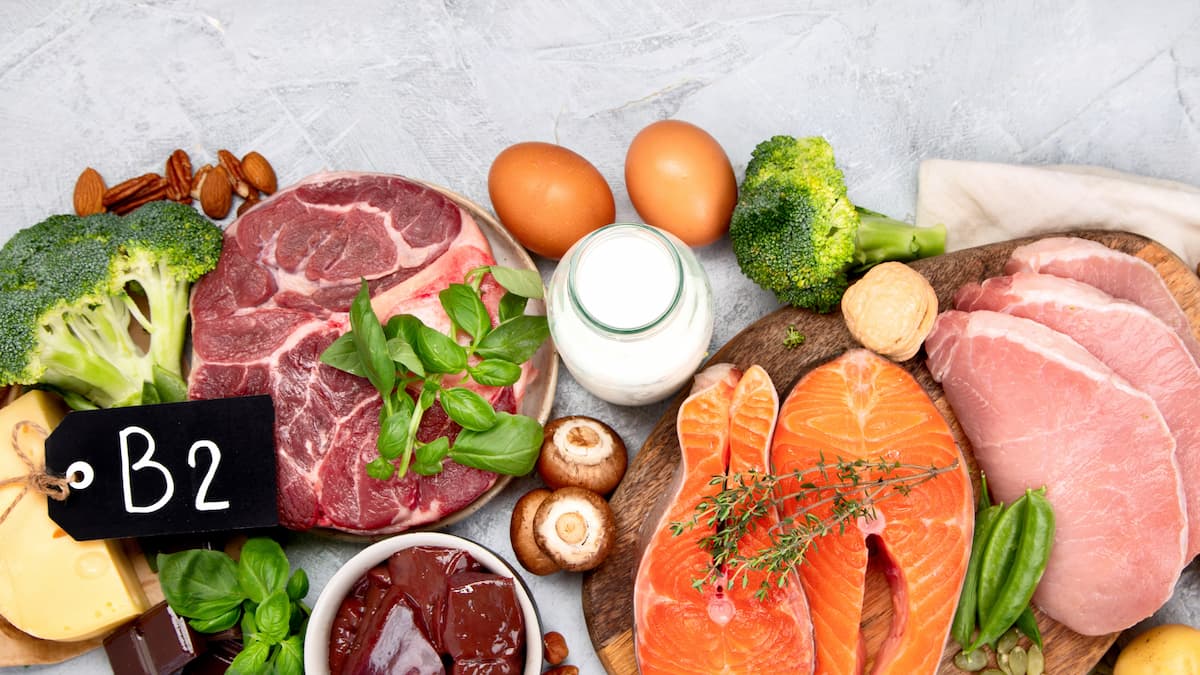
Vitamin B2 can be found in meat, milk, yoghurt, cheese or eggs. It is also not lacking in some vegetables. Here is a table with the 10 richest products in vitamin B2.
Products that are the richest in vitamin B2.
Products richest in vitamin B2
. .
|
Product . |
Vitamin B2 content per 100 grams |
|
Cooked lamb liverand |
5.27 mg . |
|
Dried seaweedand |
3.67 mg |
|
Fried beef liverand |
3.42 mg |
|
Dried pasilla peppersand |
3.20 mg |
|
Dried parsleyand |
2.38 mg . |
|
Dried ancho peppersand |
2.26 mg |
|
Liophilised chivesand |
1.50 mg . |
|
Dried corianderand |
1.50 mg |
|
Bran flakesand |
1.40 mg . |
|
Dried shiitake mushroomsand |
1.27 mg . |
Vitamin B2 deficiency
.
Vitamin B2 deficiency in developed countries is rareand. It is much more common in developing countries located in Africa or Asia. Some people are particularly vulnerable to vitamin B2 deficiency. In most cases, an unbalanced diet leads to it, but there is more to it than that.
Vitamin B2 deficiencyand vitamin B2 most commonly affects:
- seniors, .
- alcoholics, .
- vegans, .
- women taking birth control pills, .
- people with liver disorders, .
- people suffering from chronic diarrhoea, .
- pregnant and breastfeeding women, .
Vitamin B2 is thermostable but photosensitive. People treated with light are at risk of deficiency. At risk are newborns with jaundice, people with skin diseases and abusers of tanning beds..
 .
.
Julia SkrajdaDietitian
.Symptoms
.
The risk of vitamin B2 deficiency is low. Nevertheless, it is worth knowing its symptoms in order to combat the lack of this valuable vitamin in the body in time.
Symptoms of vitamin B2 deficiency:
- digestive problemsand, .
- permanent fatigue , .
- cracking at the corners of the mouth ,
- hair loss ,
- itching and redness of the eyes ,
- swelling of the mouth and throat ,
- swollen tongue ,
- skin problems , .
Effects
.
If you notice some of the above symptoms in yourself, consult your doctor immediately.
Prolonged deficiency of vitamin B2and leads to:
- anaemia, .
- cataracts, .
- problems with the reproductive system and the nervous system.
- .
To determine the concentration of vitamin B2 in the body, the glutathione reductase coefficient in erythrocytes is testedand. This is not a typical test like, for example, a blood count. It is most often ordered by a hospital, for example before a specific operation is performed. It allows us to check the risk of stroke or other cardiovascular diseases..
 .
.
Julia SkrajdaDietitian
.Vitamin B2 excess
.
Vitamin B2 is essential for the body to function properly, so we use it almost as soon as it is absorbedand. We cannot store it and are only able to absorb a limited amount of vitamin B2 at a time. Its excess is eliminated with urine, so a toxic dose has not been established.
Vitamin B2 - supplementation
.
Most of us take vitamin B2 with our diet. Nevertheless, some people (at risk of deficiency) should consider supplementation. This should not be done on its own. Although an overdose of vitamin B2 is impossibleand, any supplementation should be done under the guidance of a specialist.
If you think you may be suffering from a deficiency - look after your health and take advice from your doctor.
Vitamin B2 in pregnancy
.
Vitamin B2 is crucial for normal pregnancy development. It supports the growth of the yet-to-be-born baby , and its deficiency leads to pre-eclampsia (a complication of pregnancy that, untreated, can lead to the death of the mother or baby).
Furthermore, a lack of adequate vitamin B2 concentrations in the body can result in impaired iron absorptionand. This condition leads to anaemia.
The need for vitamin B2 increases during pregnancy and the risk of deficiency is greater then. Therefore, women who are expecting a baby should take 1.4 mg of vitamin B2 daily.
Vitamin B2 should be taken during pregnancy.
Vitamin B2 and breastfeeding
.
Vitamin B2 promotes growthand, so its adequate concentration during breastfeeding is crucial for the baby's development. Breast milk is a toddler's only source of nutrients. The requirement for vitamin B2 during breastfeeding is 1.6 mg.
.
Vitamin B2 and alcohol
.
One group at particular risk of vitamin B2 deficiency is alcohol addictsand. Drinking alcoholic beverages negatively affects the absorption of vitamin B2. Chronic alcohol consumption can lead to a deficiency of this vitamin, which manifests itself, for example, in fatigue.
Interactions of vitamin B2 with drugs
.
Vitamin B2 can interact with some medications. People taking tetracycline antibioticsand and women taking the contraceptive pilland should be particularly careful. Robust studies on the interaction of vitamin B2 with other agents are still lacking.
Caution!
.Are you taking any medications or supplements or using herbs? Under no circumstances should you decide to supplement on your own. By acting in this way, you could seriously harm your body. Only your doctor can recommend you a healthy and safe supplementation.
See also:
- Thyroid tests [which ones to do + standards + results] .
- Blood tests [how often to perform + how to prepare] .
- The liver: symptoms of diseases, functions, how to take care of it and what to avoid .
- Fatty (greasy) liver [what it is + causes + symptoms] .
- Collagen [properties + dosage] .
- Most powerful collagen [ranking + types] .
- Collagen deficiency [causes + symptoms] .
Summary
.
Remember:
.- Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) is a water-soluble B vitamin.
- Vitamin B2 is a water-soluble B vitamin.
- Vitamin B2 supports the treatment of anaemia, eye health, and also prevents headaches.
- Vitamin B2 is a water-soluble B vitamin.
- Adult women need 1.1 mg of vitamin B2 per day. Men are advised to take 1.3 mg of this compound.
- The following are the most important sources of vitamin B2.
- The most valuable source of vitamin B2 is cooked lamb liver. .
- Vitamin B2 deficiency is most common in alcoholics, vegans, seniors, women taking birth control pills, and people with malabsorption disorders.
- The following are recommended.
- A lack of vitamin B2 in the body manifests as chronic fatigue, digestive problems, itchy eyes or cracks at the corners of the mouth.
- No upper limit has been set for the intake of vitamin B2; excess is excreted in the urine. .
- Supplementation of vitamin B2 is only necessary in selected cases and should be recommended by a specialist. .
- Pregnant women are recommended to take 1.4 mg of vitamin B2 per day and breastfeeding women 1.6 mg. .
- Vitamin B2 may interact with some medications.
FAQ
.Are vitamin B2 and riboflavin the same substance?
.Yes. Vitamin B2 and riboflavin are names used to describe the same compound, which is one of the water-soluble B vitamins and affects many aspects of our body's functioning, including helping to treat anaemia, supporting eye health and exhibiting antioxidant activity.
Is vitamin B2 harmful?
.A vitamin B2 overdose is difficult to achieve as it is excreted in the urine. Unpleasant side effects, such as vomiting, nausea or abdominal pain, may occur after taking a large dose of riboflavin.
Does vitamin B2 help with migraines?
.Yes, there is scientific evidence to suggest that vitamin B2 may help relieve migraines. Several clinical trials have found that vitamin B2 supplementation of 400 mg daily (for at least three months) reduces the frequency and intensity of migraine attacks in some patients.
Which fruits contain the most vitamin B2?
.Most vitamin B2 can be found, for example, in dried bananas, apples, peaches, plums or durian (an exotic fruit with a characteristic smell). Avocados, passion fruit, kumquat and grapes are also worth a look in your daily diet.
.How often to take vitamin B2?
.The average requirement for vitamin B2 is 1.1 mg in women and 1.3 mg in men. This may vary depending on age, health status or physical activity undertaken. Larger doses of vitamin B2 are needed for the treatment of migraine pain, among other things - a doctor may prescribe a dose as high as 60-400 mg.
Whether vitamin B2 helps with aphthous stomatitis
.Jacomas are manifested by, among other things, cracked corners of the mouth. They are led by a deficiency of vitamin B2. Restoring the correct concentration of this vitamin, can help to fight against the formation of acrimonias.
How to check the level of vitamin B2 in the body
.You can check your vitamin B2 level with a blood test. The test requires no special preparation and can be taken at any time of day. You do not need to be fasting.
.
Resources
.See all
.Ahn, H., & Lee, G.-S. (2020). Riboflavin, vitamin B2, attenuates NLRP3, NLRC4, AIM2, and non-canonical inflammasomes by the inhibition of caspase-1 activity. Scientific Reports, 10(1), Article 1. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-76251-7
Ashoori, M., & Saedisomeolia, A. (2014). Riboflavin (vitamin B2) and oxidative stress: A review. British Journal of Nutrition, 111(11), 1985-1991. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114514000178
Boehnke, C., Reuter, U., Flach, U., Schuh-Hofer, S., Einhäupl, K. M., & Arnold, G. (2004). High-dose riboflavin treatment is efficacious in migraine prophylaxis: An open study in a tertiary care centre. European Journal of Neurology, 11(7), 475-477. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2004.00813.x
Mahabadi, N., Bhusal, A., & Banks, S. W. (2022). Riboflavin Deficiency. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470460/
Namazi, N., Heshmati, J., & Tarighat-Esfanjani, A. (2015). Supplementation with Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) for Migraine Prophylaxis in Adults and Children: A Review. International Journal for Vitamin and Nutrition Research. Internationale Zeitschrift Fur Vitamin- Und Ernahrungsforschung. Journal International De Vitaminologie Et De Nutrition, 85(1-2), 79-87. https://doi.org/10.1024/0300-9831/a000225
Office of Dietary Supplements-Riboflavin. (n.d.). Retrieved 17 March 2023, from https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Riboflavin-Consumer/
Peechakara, B. V., & Gupta, M. (2022). Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin). In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525977/
.Powers, H. J. (2003). Riboflavin (vitamin B-2) and health. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 77(6), 1352-1360. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/77.6.1352
Riboflavin. (2014, April 22). Linus Pauling Institute. https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/vitamins/riboflavin
Riboflavin Deficiency-An overview | ScienceDirect Topics. (n.d.). Retrieved 17 March 2023, from https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/pharmacology-toxicology-and-pharmaceutical-science/riboflavin-deficiency
Sanches, S. C., Ramalho, L. N. Z., Mendes-Braz, M., Terra, V. A., Cecchini, R., Augusto, M. J., & Ramalho, F. S. (2014). Riboflavin (vitamin B-2) reduces hepatocellular injury following liver ischaemia and reperfusion in mice. Food and Chemical Toxicology: An International Journal Published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association, 67, 65-71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2014.02.013
Suwannasom, N., Kao, I., Pruß, A., Georgieva, R., & Bäumler, H. (2020a). Riboflavin: The Health Benefits of a Forgotten Natural Vitamin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(3), 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030950
Suwannasom, N., Kao, I., Pruß, A., Georgieva, R., & Bäumler, H. (2020b). Riboflavin: The Health Benefits of a Forgotten Natural Vitamin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(3), 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030950
Thakur, K., Tomar, S. K., Singh, A. K., Mandal, S., & Arora, S. (2017). Riboflavin and health: A review of recent human research. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 57(17), 3650-3660. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2016.1145104
.
Editorials
Meet the team


Editor
Graduate of Journalism and Artes Liberales at the University of Warsaw. Since 2017, he has been working with the biggest portals in Poland and abroad as an editor. Previously worked for 3 years in one of the leading pharmaceutical companies - he knows the health and beauty industry inside out. In his free time, he most enjoys playing tennis or skiing.
![Vitamin B12 - where it occurs in the diet and in products [table].](https://cdn-resources.natu.care/uploads/1/balanced_diet_nutrition_healthy_eating_concept_food_sources_rich_vitamin_b12_cobalamin_kitchen_table_1_b84f75bda2.jpg)
Find out where vitamin B12 is found and which products will provide you with it.

Vitamin PP also known as niacin or vitamin B3 supports the proper functioning of the body.
![What is NMN? Effects, effects, side effects [supplements].](https://cdn-resources.natu.care/uploads/1/science_background_with_molecule_atom_abstract_structure_science_medical_background_3d_illustration_1_a5ec4d9cec.jpg)
Everything you want to know about NMN: properties, effects, safety and expert opinions.