Folic acid (vitamin B9) - what it is, properties, requirement, deficiency
Folic acid supports the nervous and cardiovascular systems and also influences growth.


Learn more about our editorial process
.

Learn more about our editorial process
.

Learn more about our editorial process
.

Learn more about our editorial process
.
Why you can trust us
Articles on Natu.Care are written based on scientific research, data from government websites and other reliable sources. The texts are written in cooperation with doctors, nutritionists and other health and beauty experts. Articles are reviewed before publication and during significant updates.
.Learn more about our editorial process
.Information about advertisements
Content on Natu.Care may contain links to products from the sale of which we may receive a commission. When creating content, we adhere to high editorial standards and take care to be objective about the products discussed. The presence of affiliate links is not dictated by our partners, and we select the products we review ourselves completely independently.
.Learn more about our terms and Conditions
.Folic acid, also known as vitamin B9, is essential for the formation of red blood cells. It also influences cell function and is responsible for healthy growth. Called the vitamin of mums-to-be, folic acid is crucial for early pregnancy.
Chemical, treacherous and even deadly. That's what the name folic acid sounds like, right? In reality, it is nothing to fear. The name comes from the Latin word 'folium' meaning 'leaf'. This is no coincidence, as the largest deposits of folic acid are found in leafy vegetables. Would you like to know which ones? Or are you interested in the valuable properties of vitamin B9? Are deficiencies and excesses on your agenda? You will find this and other information in this article!
Description of contents:
- What is folic acid? .
- Vitamin B9 - properties .
- Vitamin B9 in pregnancy .
- Folic acid requirements .
- Sources of vitamin B9 .
- Folic acid deficiency .
- Folic acid excess .
- Folic acid - supplementation .
- Vitamin B9 and alcohol .
- Interactions of folic acid with medications .
- Summary .

Odkryj, co dla Twojej urody może zrobić Natu.Care Glow Stories
Skóra, włosy, paznokcie: Glow Stories
Wesprzyj prawidłowy stan skóry, włosów i paznokci i ochroń komórki przed stresem oksydacyjnym!
Sprawdź cenę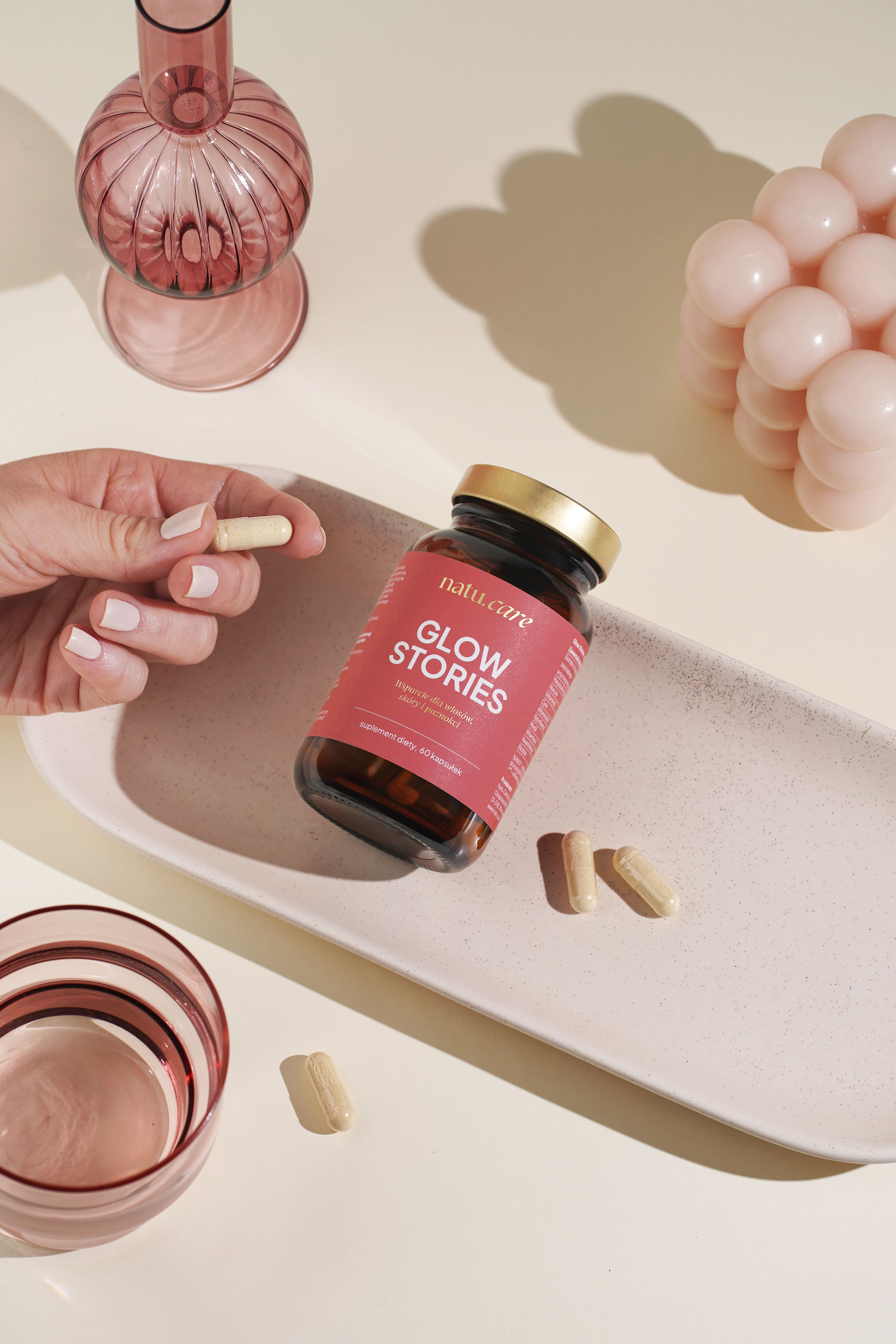
Glow Stories to formuła aktywnych składników, które zostały starannie dobrane wedle najnowszych badań naukowych. Znajdziesz w nich biotynę, cynk i miedź pielęgnujące zdrowie włosów i promiennej cery. Ponadto cynk jest odpowiedzialny także za zachowanie zdrowych paznokci. Mądra suplementacja zadba o Twoje piękno od środka.Julia Skrajda, dietetyk kliniczny
See also:
- B vitamins [properties + where they occur] .
- Vitamin B1 (thiamine) [properties + where it occurs] .
- Vitamin B2 [properties + where it occurs] .
- Vitamin B3 [properties + where it occurs]
- Niacin [what it is + effects and side effects] .
- Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) [what it is + properties and excess] .
- Vitamin B6 [where it occurs + deficiency, excess and properties]
- Biotin [what it is + properties and side effects] .
- Biotin for hair [what it gives and effects + ranking]
- Vitamin B12 [what it helps with + where it occurs] .
- Vitamin C [properties + dosage] .
- Magnesium [what it is in + properties] .
- Best magnesium [ranking + pharmacist's opinion] .
What is folic acid?
.
Folic acid (vitamin B9) is a water-soluble B vitamin. It is responsible for the formation of new cells in the body and also affects pregnancy. We are unable to produce the valuable vitamin B9, so it must be taken with the diet. Most folic acid can be found in leafy vegetables, beans or sunflower seedsand.
Folic acid is a synthetic form of vitamin B9. In nature, this vitamin is found in the form of folate. Folic acid influences homocysteine metabolism, haematopoietic processes and regulates cell growth and function..
.
What else do we call vitamin B9?
.
Folic acid is called in many different ways. Are you confused? I'm already rushing to the answers. Folic acid and vitamin B9 are the two most common names for this compound. Interestingly, it is also referred to as vitamin B11 or folacin. Slightly less common are terms such as vitamin of mums-to-be, vitamin M or listic acidand.

Glow Stories - for healthy skin, hair and nails
.Product with high-quality folic acid Quatrefolic®, bamboo shoot extract and ingredients that have a positive effect on skin, hair and nails.

Sleep Well - dietary supplement for good sleep and tranquillity
.Sleep Well is a calming and relaxing dietary supplement with a standardised complex of CALMOMIX® herbal extracts and high-quality magnesium.
Folic acid - properties
.
Despite its beautiful name, it is not the names that make vitamin B9 stand out. It's its valuable properties that make it worth taking a closer look.
How does folic acid work?
.
Influences on pregnancy health
.
Folic acid plays an important role in the development of the baby. It is responsible for cell division and tissue growth. Vitamin B9 is essential for the proper development of the spine and brain of the yet-to-be-born baby. Folic acid is also important for mothers-to-be - it reduces the risk of pre-eclampsia, as well as premature birthand.
Promotes brain health
.
Low levels of folic acid lead to impaired mental function and also increase the risk of dementia. Research suggests that vitamin B9 supplementation has a positive effect on cognitive function. Furthermore, adequate concentrations of folic acid may prevent Alzheimer's diseaseand.
Reduces risk of heart disease
.
High levels of homocysteine increase the risk of heart disease. According to research, folic acid supplementation can reduce its concentration and thus reduce the risk of heart disease. Furthermore, an analysis of a study of 80,000 people found that taking vitamin B9, reduces the risk of heart disease by 4% and the likelihood of stroke by 10%and.
Omega acids, especially omega-3 also reduce the risk of heart disease. Are you interested in these topics? Take a look at these articles!
Cures mental illnesses
.
Drinking too little folic acid leads to depression, schizophrenia, as well as other mental problems. People with depression have been shown to have lower levels of vitamin B9. A review of 2022 studies suggests that folic acid supplementation alleviates symptoms of schizophrenia, postpartum depression or bipolar disorderand.
Prevents fertility problems in women
.
Vitamin B9 has a positive effect on fertility. In women who supplemented with folic acid, it prevented neural tube defects and was also associated with a lower risk of infertility or pregnancy loss. Interestingly, supplement vendors assert that their products will improve sperm quality in men. Studies suggest, however, that folic acid does not increase fertility in menand.
How else does folic acid workand?
.
- Reduces the risk of oesophageal cancer. .
- Has a beneficial effect on insulin resistance.
- Performs a positive effect on insulin resistance.
- Has a positive effect on inflammation.
- Has a positive effect on inflammation.
Dr Jacob's Melatonin + B12

- Active ingredients: melatonin, vitamin B12
- Form: sucking pastilles .
- Dosage: 1 lozenge per day .
- Sufficient for: 60 days .
Product description
Sweet pleasures in the evening are rather forbidden. Well, unless it's cherry lozenges with melatonin and vitamin B12, whichóre going to improve the quality of your sleep.
One tablet in the evening will shorten your sleep time and stop you waking up.
One tablet in the evening will shortenóyour time to fall asleep and stop you waking up during the night. The addition of vitamin B12 will improve the functioning of the nervous system, making you even better rested.
The following tablets will help to improve the quality of your sleep.
Pros and cons
Sweet pleasures in the evening are rather forbidden. Well, unless it's cherry lozenges with melatonin and vitamin B12, whichóre going to improve the quality of your sleep.
One tablet in the evening will shorten your sleep time and stop you waking up.
One tablet in the evening will shortenóyour time to fall asleep and stop you waking up during the night. The addition of vitamin B12 will improve the functioning of the nervous system, making you even better rested.
The following tablets will help to improve the quality of your sleep.
Additional information
Sweet pleasures in the evening are rather forbidden. Well, unless it's cherry lozenges with melatonin and vitamin B12, whichóre going to improve the quality of your sleep.
One tablet in the evening will shorten your sleep time and stop you waking up.
One tablet in the evening will shortenóyour time to fall asleep and stop you waking up during the night. The addition of vitamin B12 will improve the functioning of the nervous system, making you even better rested.
The following tablets will help to improve the quality of your sleep.
User review
Sweet pleasures in the evening are rather forbidden. Well, unless it's cherry lozenges with melatonin and vitamin B12, whichóre going to improve the quality of your sleep.
One tablet in the evening will shorten your sleep time and stop you waking up.
One tablet in the evening will shortenóyour time to fall asleep and stop you waking up during the night. The addition of vitamin B12 will improve the functioning of the nervous system, making you even better rested.
The following tablets will help to improve the quality of your sleep.
SOLGAR natural vitamin B12

- Active ingredients: vitamin B12
- Form: tablets .
- Packaging: 100 tablets .
- Dose: 1 tablet daily .
- Sufficient for: 100 days .
Product description
The dietary supplement is a source of valuable vitamin B12 in a form that is easily absorbed by humans - cyanocobalamin. This biologically active form of vitamin B12 has many very important protective functions for the body.
Vitamin B12 supports the functioning of the immune system. It also contributes to reducing feelings of fatigue and tiredness. Its important function is also to take part in the metabolism of homocysteine, an amino acid thatós naturally formed in the human body.
Vitamin B12 is a very important protective function.
Pros and cons
The dietary supplement is a source of valuable vitamin B12 in a form that is easily absorbed by humans - cyanocobalamin. This biologically active form of vitamin B12 has many very important protective functions for the body.
Vitamin B12 supports the functioning of the immune system. It also contributes to reducing feelings of fatigue and tiredness. Its important function is also to take part in the metabolism of homocysteine, an amino acid thatós naturally formed in the human body.
Vitamin B12 is a very important protective function.
Additional information
The dietary supplement is a source of valuable vitamin B12 in a form that is easily absorbed by humans - cyanocobalamin. This biologically active form of vitamin B12 has many very important protective functions for the body.
Vitamin B12 supports the functioning of the immune system. It also contributes to reducing feelings of fatigue and tiredness. Its important function is also to take part in the metabolism of homocysteine, an amino acid thatós naturally formed in the human body.
Vitamin B12 is a very important protective function.
User review
The dietary supplement is a source of valuable vitamin B12 in a form that is easily absorbed by humans - cyanocobalamin. This biologically active form of vitamin B12 has many very important protective functions for the body.
Vitamin B12 supports the functioning of the immune system. It also contributes to reducing feelings of fatigue and tiredness. Its important function is also to take part in the metabolism of homocysteine, an amino acid thatós naturally formed in the human body.
Vitamin B12 is a very important protective function.
Aura Herbals Vitamin B Complex drops
Product description
Vegan drops with a complex of B vitamins. A daily serving covers 100% of the requirement for these vitamins. B vitamins are important for the proper functioning of the body, especially for the nervous system, metabolism and energy production.
Pros and cons
Vegan drops with a complex of B vitamins. A daily serving covers 100% of the requirement for these vitamins. B vitamins are important for the proper functioning of the body, especially for the nervous system, metabolism and energy production.
Additional information
Vegan drops with a complex of B vitamins. A daily serving covers 100% of the requirement for these vitamins. B vitamins are important for the proper functioning of the body, especially for the nervous system, metabolism and energy production.
Folic acid in pregnancy
.
Folic acid is very important for the health of pregnancy. It is a true superhero that prevents numerous fetal birth defectsand.
Folic acid is extremely important before and during pregnancy. It prevents neural tube defects in the foetus..
Carolina Król-Lach Dietitian
When to adopt?
.
Contrary to appearances, vitamin B9 should not remain of interest only to pregnant ladies. Adequate levels of folic acid must be taken care of by every woman of childbearing age. Birth defects already develop during the first three to four weeks of pregnancy, when it may still be undetected. This is why it is necessary to ensure adequate folic acid concentrations even before pregnancyand.
How much vitamin B9 to take?
.
The recommended dose of folic acid for women of childbearing age does not differ from the basic recommendation and is 400 mcg per day. For the first 3 months of pregnancy, this amount will also meet the needs of the mother-to-be and the baby. Once you enter the 4th month of pregnancy, however, the dose needs to be increased. It is then necessary to take 600 mcg of vitamin B9 per dayand.
Wondering if you are pregnant? Not sure if you especially need to ensure that you are getting enough folic acid in your body? Take a look at the article on pregnancy symptoms!
What does it affect?
.
Lack of adequate folic acid during pregnancy leads to neural tube defects. The most common of these include brainlessness, i.e. incomplete development of the major components of the brain. In most cases, children with this defect are at serious risk of death. Another problem can be spina bifida leading to permanent disabilityand.
Folic acid taken during pregnancy also protects againstand:
.
- .
- pornation, .
- low birth weight, .
- splitting of the lip and palate, .
- restricted foetal growth,
- premature birth, and
- premature birth, .
See also:
Folic acid requirements
.
The amount of folic acid you should take each day depends on your age. What are the recommended dosages for each groupand?
|
Age . |
Recommended daily intake of folic acid* . |
|
0-6 months |
65 mcg |
|
7-12 months |
80 mcg |
|
1-3 years |
150 mcg |
|
4-6 years |
200 mcg |
|
7-12 years |
300 mcg |
|
13+ years |
400 mcg |
*Nutrition standards for the Polish population
.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women have an increased requirement for vitamin B9. Ladies who are expecting a baby should take 600 mcg of folic acid daily. Breastfeeding women, on the other hand, only need a dose of 500 mcg of vitamin B9and.
Sources of vitamin B9
.
Carolina Król-Lach stresses that in a diet rich in vitamin B9, it is worth ensuring the presence of spinach, broccoli, savoy cabbage, as well as pulses. Inactive yeast flakes are also a valuable source and are a great substitute for cheese flavour in vegan dishes. Not keen on these foods? Check out the 10 foods richest in folic acidand!
.
|
Product . |
Folic acid content per 100 grams . |
|
| . |
Bran flakes |
648 mcg . |
|
Dried green mint |
530 mcg |
|
|
Lentils |
479 mcg . |
|
|
Lamb liver . |
400 mcg . |
|
|
Edamame . |
311 mcg |
|
|
Dried basil . |
310 mcg |
|
|
Dried rosemary |
307 mcg . |
|
|
Dried coriander |
274 mcg . |
|
|
Dried marjoram |
274 mcg . |
|
|
Milled sage |
274 mcg . |
Good sources of folate are vegetables (especially green vegetables) and cereal products. High temperature destroys the folates found in food. Cooking for more than 15 minutes practically completely loses folate, so fresh or short-cooked vegetables should be included in the diet.
Carolina Król-Lach Dietitian
.
In addition to sensitivity to heat treatment, folic acid is also negatively affected by UV rays. Therefore, products and supplements with vitamin B9 should be stored in a cool and shaded place. In addition to the aforementioned products, folic acid is also present in egg yolk and nuts (mainly almonds)..
 .
.
Julia Skrajda Clinical nutritionist
Folic acid deficiency
.
Vitamin B9 accumulates mainly in the liver. However, its deposits are usually negligible and amount to around 5 mg. This is an amount sufficient for 3-4 monthsand. Therefore, one of the main aspects that leads to its deficiency is a poor diet. What else leads to a lack of folic acid in the body?
Causes of vitamin B9 deficiency in the bodyand:
- Excessive alcohol consumption. .
- Diseases of the digestive system, such as celiac disease or Crohn's disease.
- Diseases of the digestive system, such as celiac disease or Crohn's disease.
- Hemolytic anaemia. .
- Taking antiepileptic drugs or other agents that interfere with the absorption of folic acid. .
- Eating overcooked vegetables and fruits (they then lose folic acid). .
- Dialysis of the kidneys. .
Alcohol abusers, cigarette smokers, pregnant women, ladies using hormonal contraception, adolescents during puberty, infants (especially those with low birth weight), seniors, and people with gastrointestinal diseases are at risk of deficiency.
Folic acid deficiency is a major concern.
In the body, folic acid is converted to its biologically active form. Therefore, its deficiency can also occur in people who have a disorder in the metabolism of folic acid (this is genetically determined). In this situation, supplementation with the methylated form of folic acid is recommended..
Carolina Król-Lach Dietitian
.The need for B9 supplementation is also present in people with the MTHFR C677>T or A1298>C gene polymorphism (this variant is most common in Poles). The MRHFR gene is required for the formation of the enzyme of the same name. This enzyme is responsible for converting ingested folic acid into the active form, ready to be assimilated by our body.".
 .
.
Julia Skrajda Clinical nutritionist
.Symptoms
.
One of the main symptoms of vitamin B9 deficiency is constant fatigue. However, this is not the only symptom that should cause us concern.
Symptoms of folic acid deficiencyand:
- dizziness, .
- spiration, .
- irritability, .
- difficulty concentrating, .
- disorientation, .
- lack of energy, .
- weakened muscles, .
- diarrhoea, .
- unexplained weight loss, .
People with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are at risk of deficiency, both because of the deterioration of absorption and the effect of sulfasalazine, often used in their treatment. Deterioration of absorption also occurs in people with coeliac disease and after bariatric surgery..
Karolina Król-Lach Dietitian
Effects
.
Deficiency of folic acid can be very dangerous in the long term. Vitamin B9 is crucial for the health of the body. Therefore, it is important to ensure its adequate concentration. Untreated folic acid deficiency leads toand:
- depression, .
- dementia, .
- fertility problems, .
- reduced cognitive function, .
Folic acid deficiencies lead to megaloblastic anaemia, digestive disorders, decreased appetite, inflammation of the membranes of the tongue or the mucous membranes of the lips (so-called "cavities" appear).
Because vitamin B9 is important for the proper functioning of the nervous system, a deficiency of this vitamin can lead to feelings of fatigue, impaired concentration, increased anxiety, restlessness, irritability and insomnia. In children and adolescents, a deficiency can lead to stunted growth..
Karolina Król-Lach Dietitian
Folic acid excess
.
Vitamin B9 excess is not common. In most cases, it is caused by taking too much in supplements. Nevertheless, taking more than 1000 mcg of folic acid per day can lead to symptoms of vitamin B9 excessand. Which ones?"
Excess folic acid also negatively affects our health. With too much, insomnia, irritability, gastrointestinal disorders and allergic reactions can occur..
Carolina King-Lach Dietitian
.Mask vitamin B12 deficiency
.
Excess vitamin B9 can lead to masking vitamin B12 deficiency. Vitamin B12 is essential for the production of red blood cells, as well as maintaining the health of the nervous system, brain or heart. Untreated B12 deficiency can result in irreversible nerve damageand.
Taking too much folic acid can mask megaloblastic anaemia, a condition caused by vitamin B12 deficiency. Symptoms that can occur with this condition include fatigue, general weakness or concentration problems .
Slows development in children
.
Adequate folic acid concentrations are crucial for foetal health. Research suggests that babies whose mothers took in more than 1,000 mcg of vitamin B9 per day during pregnancy had lower developmental test scores than babies whose parents took in 400-999 mcg of folic acidand.
What's more, high doses of folic acid taken during pregnancy have been linked to a greater risk of insulin resistance at age 9-13 years.
Increases mental decline that progresses with age
.
Some studies suggest a link between high folic acid levels and mental impairment in people over 60 years of age. In contrast, other tests indicate that people with vitamin B12 deficiency and high levels of vitamin B9 had about 3.5 times the risk of loss of brain function than seniors with normal bloodand.
Warning box!
.Supplement folic acid only when recommended by your doctor. Take it under the guidance of a specialist to safely enjoy the benefits it offers us.
Folic acid - supplementation
.
Most people absorb an adequate amount of folic acid with their diet. This is why supplementation is rarely necessary. It is most often recommended to pregnant and breastfeeding women. Sometimes supplements should also be supported by people who have a poor diet or suffer from diseases that interfere with the absorption of vitamin B9and.
Clinical nutritionist Julia Skrajda says the following about folic acid:
.
- Folic acid is a synthetic, inactive form of folate. This means that the body can only utilise its valuable properties after the entire metabolic process. Methylfolate (the active form of vitamin B9) is much better absorbed. It is most commonly found under the name Quatrefolic®. .
- It is the best choice when it comes to folic acid supplementation. Quatrefolic® passes through the gastric barrier and is mainly absorbed in the small intestine. .
- Furthermore, it is a reduced and water-soluble form and is therefore better absorbed by mucosal cells. This translates into access to the blood and circulatory system.
How long to take?
.
Folic acid is one of the water-soluble vitamins. That is why there is nothing to prevent you from taking it at any time of the day. Some doctors recommend, however, that you do so shortly after waking up. Energy production and nutrient metabolism are processes for which B vitamins are responsibleand.
Folic acid levels can be a marker of gut health (as can B12, iron and ferritin levels). It is not uncommon for low levels of vitamin B9 to occur in inflammatory bowel disease, coeliac disease, parasitic diseases and gastrointestinal candidiasis (the latter two being mainly a problem for women). In these conditions, the body has an increased need for folic acid. Therefore, its supply with food alone is not sufficient. Supplementation is necessary..
 .
.
Julia Skrajda Clinical nutritionist
.Contraindications
.
Despite its numerous health-promoting properties, folic acid should not be taken by everyone. Who belongs to this group?
Folic acid should not be taken byand:
.
- persons who have an allergy to vitamin B9 or certain components of the supplements, .
- sufferers of vitamin B12 deficiency, .
- persons taking certain medications, .
Supplementation of folic acid should be combined with foods rich in vitamin C, iron, zinc and vitamin B12. These compounds significantly increase the absorption of vitamin B9..
 .
.
Julia Skrajda Clinical nutritionist
.Vitamin B9 and alcohol
.
Excessive consumption of alcohol negatively affects the absorption of folic acid in the body. Furthermore, more often than not, people who consume alcohol in large quantities have a poor diet that does not provide them with adequate amounts of vitamin B9. Research suggests that four out of five people with alcohol dependence are folic acid deficientand.
Interactions of folic acid with drugs
.
Vitamin B9 can interact with a variety of medications. Are you taking any medication? Under no circumstances take folic acid on your own. Only your doctor can recommend a healthy and safe supplementation for you. Who should be particularly careful?
Folic acid may interact withand:
- methotrexate, .
- pyrimethamine, .
- barbiturates, .
- antiepileptic drugs, such as phenytoin, carbamazepine or sodium valproate,
- sulfasalazine.
- sulfasalazine, .
Note!
.Are you taking these or other medications? Healthy supplementation can only be recommended to you by your doctor. It's your health, take care of it and don't listen to the advice of "experts" who tell you to "take a supplement". Consult a specialist who will suggest healthy supplementation.
See also:
Summary
.
Remember:
.- Folic acid (vitamin B9) is a water-soluble vitamin.
- Promote brain health.
- Promoting brain health, influencing the development of pregnancy or reducing the risk of heart disease are just some of the properties of folic acid.
- Promoting brain health, influencing the development of pregnancy or reducing the risk of heart disease are just some of the properties of folic acid.
- Most vitamin B9 can be found in bran flakes. .
- Folic acid deficiency manifests itself including fatigue, shortness of breath or dizziness .
- Excess vitamin B9 can mask vitamin B12 deficiency, slow down development in children, and accelerate mental decline in seniors.
- Folic acid is crucial for a healthy pregnancy.
- Alcohol interferes with vitamin B9 absorption.
- Folic acid may react with some medications.
- Folic acid may react with some medications.
FAQ
.What does folic acid help with?
.B vitamins support the whole body. Folic acid, or vitamin B9, influences female fertility and pregnancy health, supports brain function and cognitive function, aids red blood cell production, reduces the risk of heart disease and stroke, and has a positive effect on inflammation.
Is folic acid good for hair?
.Folic acid stimulates matrix cells to grow and therefore contributes to the formation of new, healthy hair and hair regeneration. It indirectly prevents hair loss and influences the preservation of natural hair colour.
See also: Best vitamins for hair - ranking and expert opinion
.Can everyone take folic acid? Who should?"
.Folic acid supplementation is most often recommended for women who are pregnant, planning pregnancy and breastfeeding mothers. Supplementation is also necessary in cases of poor diet and malabsorption. Low levels of B9 can also be a symptom of inflammatory bowel disease, coeliac disease or parasitic diseases. Folate supplementation is also worth considering in cases of fatigue, concentration problems or sleep disorders.
.Counter-indications to folic acid supplementation are primarily:
.- Allergy to vitamin B9 or the ingredients in a particular preparation, .
- vitamin B12 deficiency, .
- taking certain medications, e.g. antiepileptic drugs, methotrexate, barbiturates, pyrimethamine. .
How to supplement folic acid?
.Most vitamin B9 deficiencies can be compensated for by an adequate diet. Spinach, kale, broccoli, savoy cabbage, lentils, liver, eggs and ripened cheeses contain the highest levels of folic acid.
In situations of increased need, folic acid supplementation will be required and dosage should be discussed with your doctor.
Can folic acid be purchased without a prescription and consultation with a doctor?
.Folic acid supplements are widely available without a prescription. Although you do not need a consultation with your doctor to purchase one, it is worth doing so in order to determine the appropriate dosage based on your history and medical condition, and to avoid dangerous interactions with other medications.
How long can you take folic acid?
.The duration of folic acid supplementation depends on health status, individual needs and the purpose of supplementation. Women planning a pregnancy - after consulting their doctor - should start it several months before becoming pregnant and continue it during, varying the doses accordingly. After the start of the 4th month of pregnancy, it can be as high as 600 μg per day.
Can I overdose on folic acid?
.Vitamin B9 is water-soluble and overdose does not occur often as it is excreted in the urine. If it does occur, it can cause insomnia, allergic reactions, mask vitamin B12 deficiency, slow the development of children and increase the risk of insulin resistance.
When to take folic acid - morning or evening?
.The time of day does not affect the absorption of vitamin B9. You can take folic acid in the morning and in the evening. Some experts recommend doing it shortly after waking up, as B vitamins are responsible for energy production and metabolism.
Does coffee leach folic acid?
.Research shows that excessive coffee consumption can have a negative impact on the levels of B vitamins in the body, including folic acid. Regular coffee drinking may increase the loss of excess vitamin B by excretion through urine.
.
Sources
.See all
.Bender, A., Hagan, K. E., & Kingston, N. (2017). The association of folate and depression: A meta-analysis. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 95, 9-18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2017.07.019
CDC. (2022, September 9). Folic Acid: The Best Tool to Prevent Neural Tube Defects. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/folicacid/features/folic-acid-helps-prevent-some-birth-defects.html
Ganguly, P., & Alam, S. F. (2015). Role of homocysteine in the development of cardiovascular disease. Nutrition Journal, 14(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-14-6
GASKINS, A. J., & CHAVARRO, J. E. (2018). Diet and Fertility: A Review. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology, 218(4), 379-389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2017.08.010
Homocysteine Lowering with Folic Acid and B Vitamins in Vascular Disease | NEJM. (n.d.). Retrieved March 17, 2023, from https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/nejmoa060900
Jang, S., Han, J. W., Shin, J., Kim, T. H., Kwak, K. P., Kim, K., Kim, B. J., Kim, S. G., Kim, J. L., Kim, T. H., Moon, S. W., Park, J. Y., Park, J. H., Byun, S., Suh, S. W., Seo, J., So, Y., Ryu, S.-H., Youn, J. C., ... Kim, K. W. (2019). Normal-But-Low Serum Folate Levels and the Risks for Cognitive Impairment. Psychiatry Investigation, 16(7), 532-538. https://doi.org/10.30773/pi.2019.05.29
Lam, N. S. K., Long, X. X., Li, X., Saad, M., Lim, F., Doery, J. C., Griffin, R. C., & Galletly, C. (2022). The potential use of folate and its derivatives in treating psychiatric disorders: A systematic review. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 146, 112541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112541
Li, B., Zhang, X., Peng, X., Zhang, S., Wang, X., & Zhu, C. (2019). Folic Acid and Risk of Preterm Birth: A Meta-Analysis. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 13. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnins.2019.01284
Li, Y., Huang, T., Zheng, Y., Muka, T., Troup, J., & Hu, F. B. (n.d.). Folic Acid Supplementation and the Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Journal of the American Heart Association, 5(8), e003768. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.116.003768
Liu, C., Liu, C., Wang, Q., & Zhang, Z. (2018). Supplementation of folic acid in pregnancy and the risk of preeclampsia and gestational hypertension: A meta-analysis. Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics, 298(4), 697-704. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-018-4823-4
Ma, F., Li, Q., Zhou, X., Zhao, J., Song, A., Li, W., Liu, H., Xu, W., & Huang, G. (2019). Effects of folic acid supplementation on cognitive function and Aβ-related biomarkers in mild cognitive impairment: A randomised controlled trial. European Journal of Nutrition, 58(1), 345-356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-017-1598-5
Office of Dietary Supplements-Folate. (n.d.). Retrieved March 17, 2023, from https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Folate-HealthProfessional/
Schisterman, E. F., Sjaarda, L. A., Clemons, T., Carrell, D. T., Perkins, N. J., Johnstone, E., Lamb, D., Chaney, K., Van Voorhis, B. J., Ryan, G., Summers, K., Hotaling, J., Robins, J., Mills, J. L., Mendola, P., Chen, Z., DeVilbiss, E. A., Peterson, C. M., & Mumford, S. L. (2020). Effect of Folic Acid and Zinc Supplementation in Men on Semen Quality and Live Birth Among Couples Undergoing Infertility Treatment: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA, 323(1), 35-48. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.18714
Young, S. N., & Ghadirian, A. M. (1989). Folic acid and psychopathology. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry, 13(6), 841-863. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-5846(89)90037-7
.
Editorials
Meet the team


Editor
Graduate of Journalism and Artes Liberales at the University of Warsaw. Since 2017, he has been working with the biggest portals in Poland and abroad as an editor. Previously worked for 3 years in one of the leading pharmaceutical companies - he knows the health and beauty industry inside out. In his free time, he most enjoys playing tennis or skiing.
![Vitamin B12 - where it occurs in the diet and in products [table].](https://cdn-resources.natu.care/uploads/1/balanced_diet_nutrition_healthy_eating_concept_food_sources_rich_vitamin_b12_cobalamin_kitchen_table_1_b84f75bda2.jpg)
Find out where vitamin B12 is found and which products will provide you with it.

Vitamin PP also known as niacin or vitamin B3 supports the proper functioning of the body.
![What is NMN? Effects, effects, side effects [supplements].](https://cdn-resources.natu.care/uploads/1/science_background_with_molecule_atom_abstract_structure_science_medical_background_3d_illustration_1_a5ec4d9cec.jpg)
Everything you want to know about NMN: properties, effects, safety and expert opinions.